
Loss of Seizure Control in an Adolescent due to Carbamazepine-Induced Hypocalcemia
Background: Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) cause vitamin D deficiency through induction of hepatic microsomal enzymes. Adolescents are more vulnerable because of the added factors of their higher growth requirement.
We are reporting a case of loss of seizure control due to hypocalcemia resulting from long-term treatment with Carbamazepine.
Case summary: This 13-year-old boy with history of complex epilepsy diagnosed 3 years back, mild developmental delay, controlled on carbamazepine presented to ED with 2 days history of fever, cough and attack of generalized seizure lasted for 1-min resolved spontaneously. History revealed that he had dizziness in the last 8 weeks both in the standing and sitting positions. His carbamazepine was increased recently from14 to21mg/kg (600mg-BID)by his primary neurologist (maxim dose-1200mg/day).
His past history was uneventful except for seizures , full works up done EEG for brain showed frequent burst of spikes and slow waves. MRI-head was unremarkable. Family history is negative for any neurological disorders.
On examination he had normal vital signs; both height, weight on 50th-centile, Tanner stage-2. Physical examination was unrevealing.
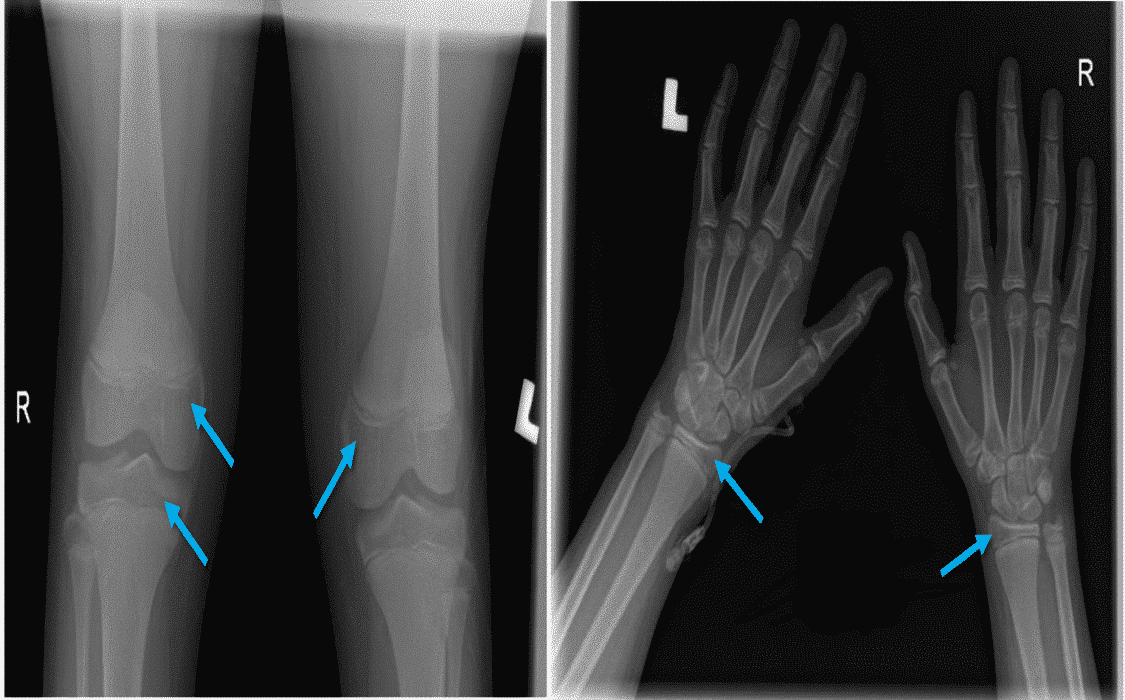
His workup showed hypocalcemia 1.64-mmol/l, high phosphorus 1.83-ng/ml, high ALP 496-U/L, low vit-D level 7-ng/ml and high PTH 228-pg/ml. Serum Na,K,Mg, albumin and liver enzymes all normal. Blood level of carbamazepine was toxic-64.4-umol/l. 12-lead ECG showed normal sinus-rhythm. X-ray of wrists and knees showed: severe decalcification of metaphysis of both.
Patient received IV calcium gluconate which raised calcium level to-1.9mmol/l and mega dose of vitamin-D3(300000 IU) Intramuscular and kept on oral calcium supplement (50-mg/kg/day). His dose of carbamazepine was reduced with total resolution of dizziness and seizure.
Conclusions: Loss of seizure control in a patient stabilized on antiepileptic drugs is an indication to check the patient`s calcium and vitamin-D-status. Proper treatment of this complication is vitamin-D and calcium supplementation. Prophylactic supplementation with vitamin-D is necessary in adolescents.
Powered by Eventact EMS