
Effect of Phytotherapy on Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients with Obesity
2Pediatrics, Royal University Hospital, Saskatoon, Canada
Obesity traditionally ontrolled by dietary restriction, exercise, and/or different types of synthetic oral
medications, and it commonly associated with dyslipidemia. We used medical herbs decoction “APFJ”
(Achillea millefolium, Phyllocladus alpinus, Frangula cortex, Juniper berries) with well‐known antioxidant
and cardioprotective properties in complex therapy of patients with obesity.
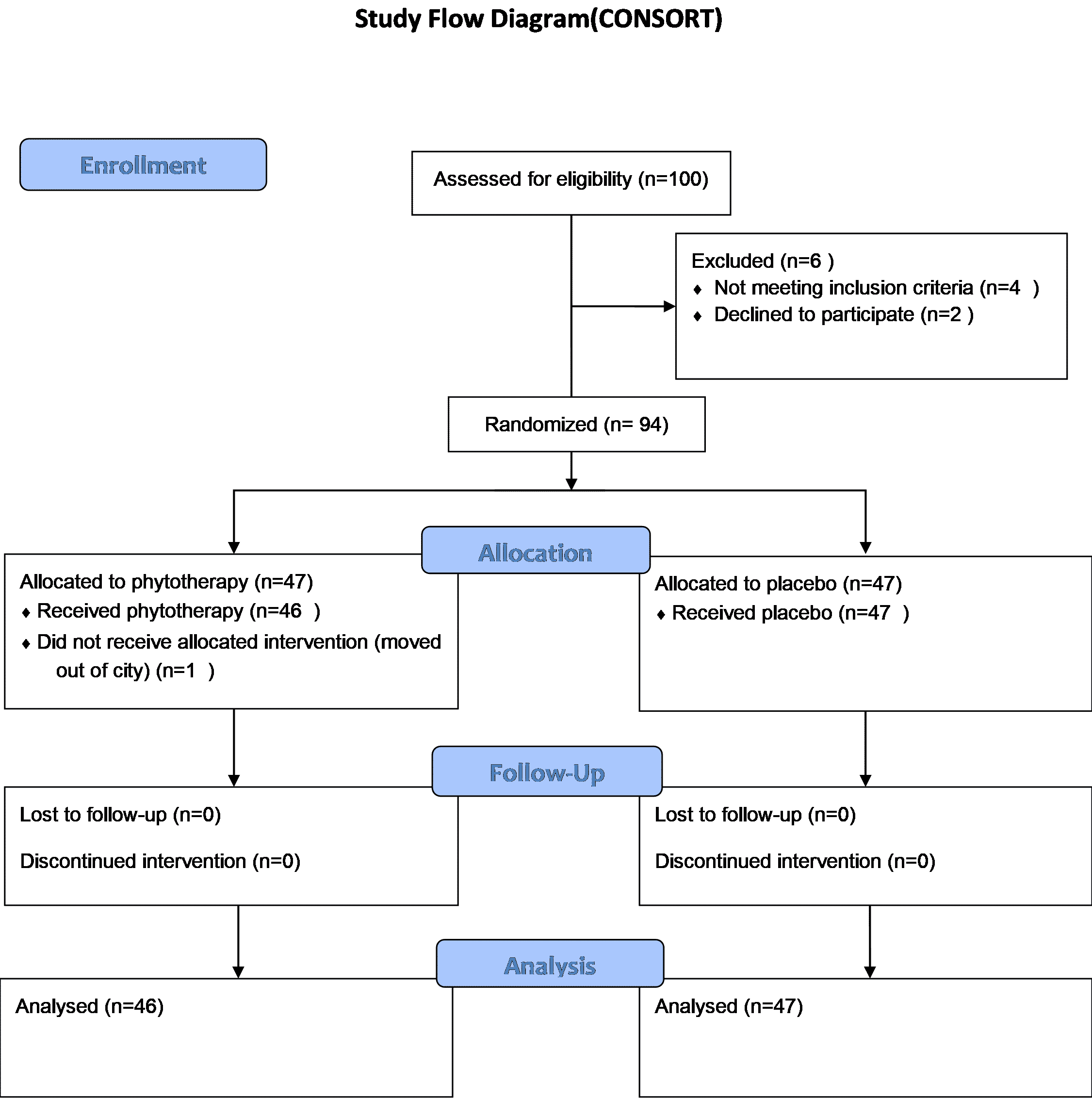
93 children aged 7-12 received traditional therapy (dietary restriction and lifestyle modification) and
herbal decoction (50 ml/day), or placebo for 12 weeks in a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Serum
concentrations of total cholesterol, triglycerides, low‐density, and high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol,
together with cardiac functions via stress echocardiography (SE) were done prior to the initiation of
therapy and after completion of the first course. Anthropometric parameters including weight, BMI body
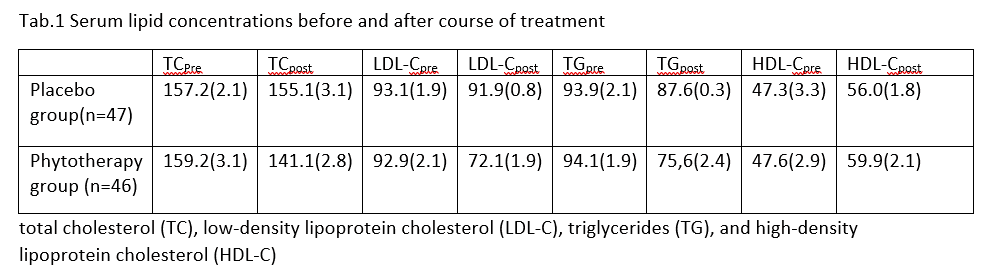
fat remained unchanged between two groups (p > 0.05). Serum triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein
levels were significantly reduced following herbal concoction administration (p = 0.008 and 0.09).
Exercise SE findings were similar in both groups. No adverse reactions were observed.
Phytotherapy could be used as add-on conventional therapy in pediatric patients with obesity.
Powered by Eventact EMS