
Awareness among Physicians and Parents towards Hand Hygiene in Relation to Coronavirus Disease COVID-19) Infection Prevention
2Pediatric, Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar
Background: Since Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection has been considered as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in February 2019, many health care organizations and facilities have extended their efforts to conduct studies about preventing its transmission among the general population and health care providers. Our aim is to study the perception of parents and doctor to hand hygiene in preventing the transmission of COVID-19 infection
Methods: A prospective cross sectional study with a total of 209 participants were enrolled and were asked to fill a paper-based survey during April 2019. The number of participants were 50 doctors, 40 nurses, 18 other health-allied staff and 50 of patients’ parents. Different educational levels ranging from people not completing high school to others who finished high education and living status taken into consideration assessing the number of household living with each participant
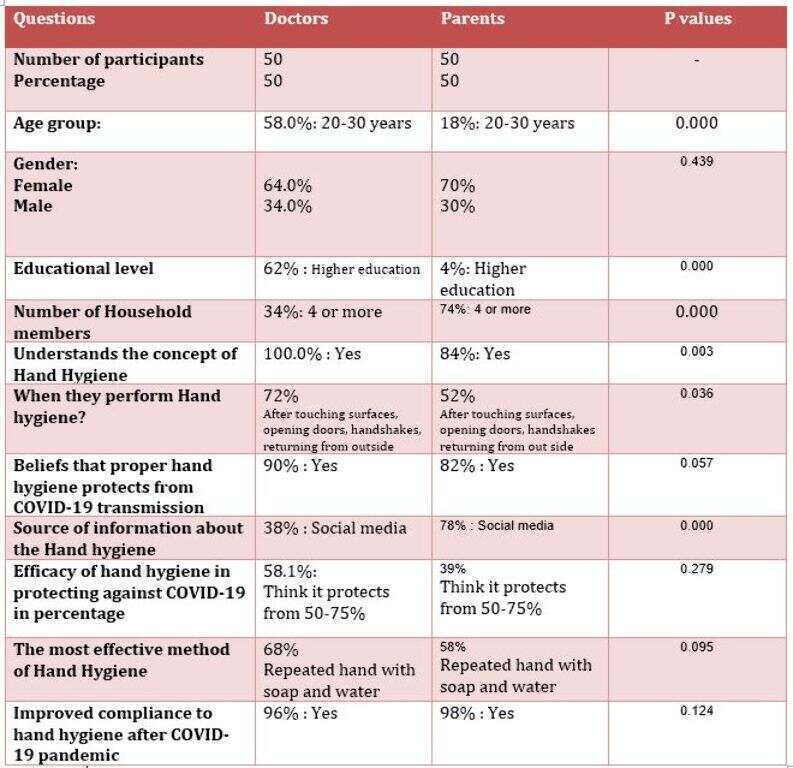
Results: After assessing the general knowledge of the participants for hand hygiene, it found that 84% of the parents believe that they know what does that mean, compared to 100% of doctors(p-value 0.002).Only52% of the parents are doing hand hygiene according to the 5-moments of hand hygiene requirement, after handshakes and opening doors or touching any surface and after coming back home, compared to 72%of the participated doctors(0.036). 82% of the parents’ beliefs that proper hand hygiene would prevent transmission of COVID-19 infection compared to 90% of doctors[p-value 0.05]
Conclusions: Social media is having a great impact on the general population awareness towards preventing the spread of COVID-19 infection. Future plan is to ameliorate efforts in using social media in order to ensure that the proper and correct measures are received by the general population towards prevention of spread of COVID-19 infection.
Powered by Eventact EMS