
Mycobacterium Marinum Infection following a Microlight Injury
2Pathology, Mater Dei Hospital, Msida, Malta
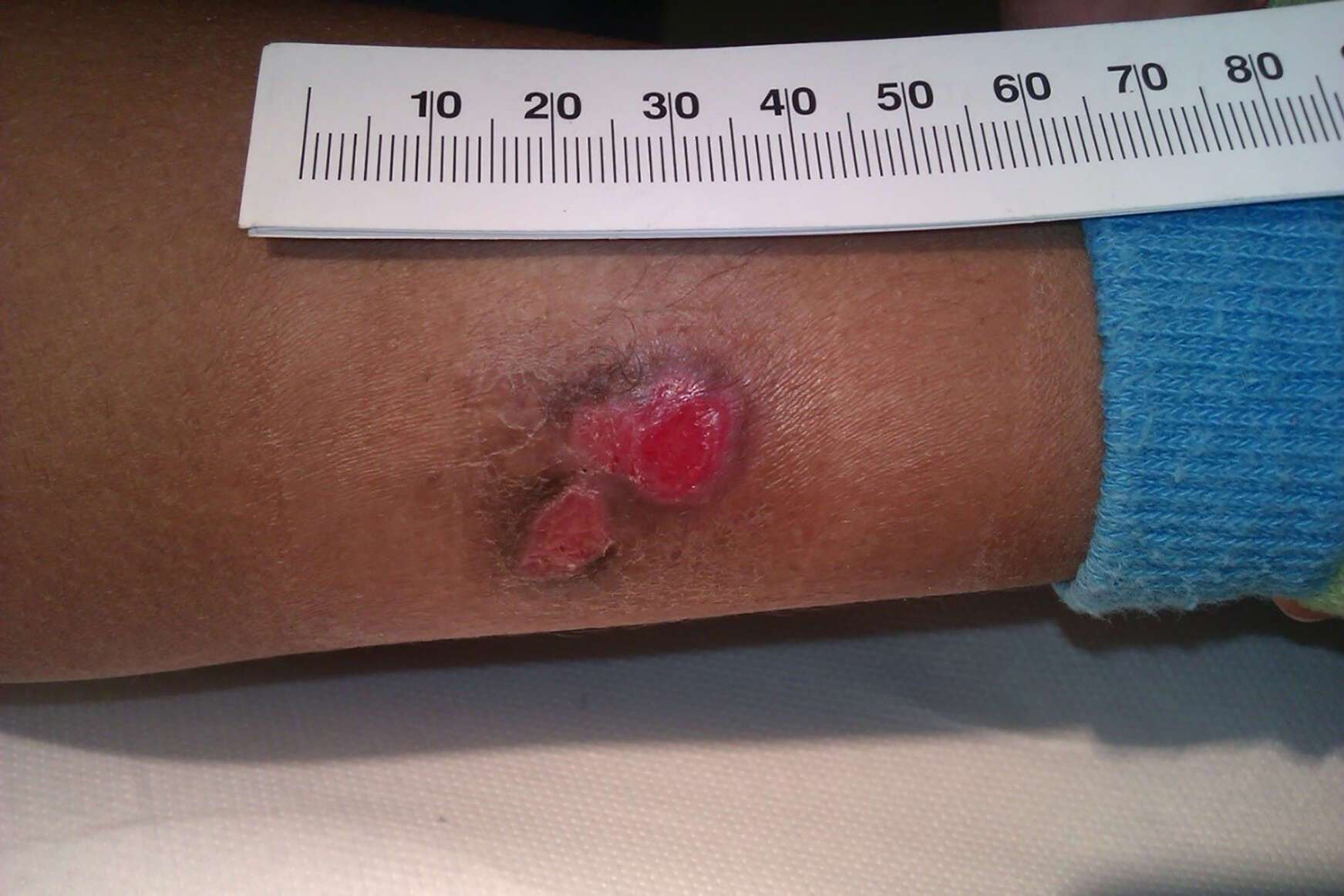
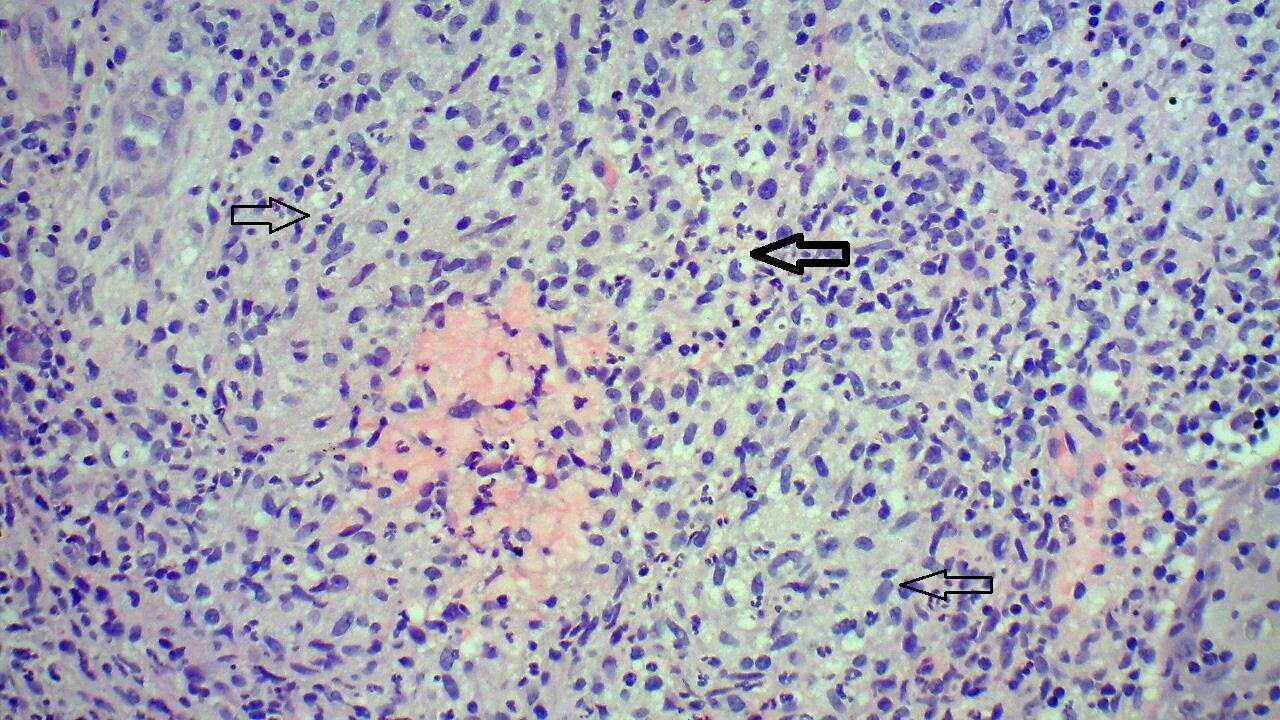
A 5 year old boy presented with a 13 month history of painless, indurated and discharging ulcers on the lateral aspect of the left leg (Figure 1a). These occurred following a penetrating injury with the front fork of a microlight which had been to Hungary, Slovenia and Italy during September before landing in Malta. There was no response to local exfoliating treatment, steroids and antibiotics. X-ray excluded bone involvement. Blood investigations including quantiferon-TB gold test and HIV were negative. Biopsy revealed granulomatous inflammation with multinucleated giant cells and acute inflammation (Figure 1b). No mycobacteria were seen on Ziehl-Neelsen staining but Mycobacterium marinum was isolated on culture. The ulcers resolved completely after 8 weeks of clarithromycin, rifampicin and ethambutol followed by a further 2 months of clarithromycin (ethambutol was stopped because of disturbances in colour vision).
M. marinum infections are uncommon in humans with an annual incidence of 0.04 – 0.27 cases per 100,000 individuals. Infection results from trauma associated with exposure to non-disinfected salt- and freshwater reservoirs. Skin and soft tissue infection occurs in 90% of cases with invasive or disseminated infection reported in older or immunocompromised patients. A two-drug regimen is advised, including a macrolide and a rifamycin, ethambutol, or co-trimoxazole, continued for 2 months following resolution. The aircraft had likely travelled through contaminated water during the start of the rainy season in Europe. A chronic non-healing ulcer following a history of penetrating trauma and water exposure should prompt consideration of M. marinum infection.
Powered by Eventact EMS