
Prevalence and prognostic significance of diastolic dysfunction among hospitalized patients referred for Echocardiography
Introduction: Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is frequent among elderly patients (pts) with cardiovascular risk factors and is related to heart failure. We assessed the prevalence and prognostic significance of LVDD among hospitalized pts referred for Echocardiography.
Methods: 3828 consecutive pts who underwent echocardiograpy, had normal/ preserved LV systolic function were included. LVDD grades I/II/II were defined according to ASE/EACVI 2016 recommendations. Mortality data were derived from the Israel National Population Registry.
Results: Clinical Characteristics
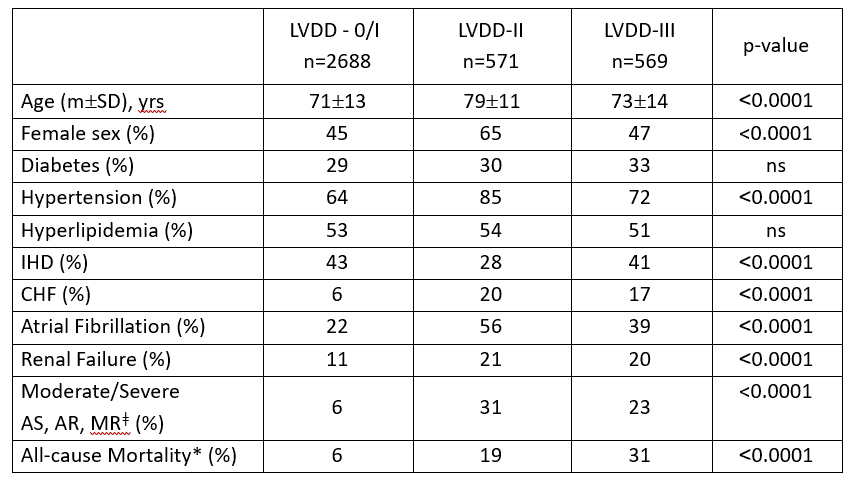
ǂAortic Stenosis, Aortic Regurgitation, Mitral Regurgitation
*Median follow up time 294(101-617) days
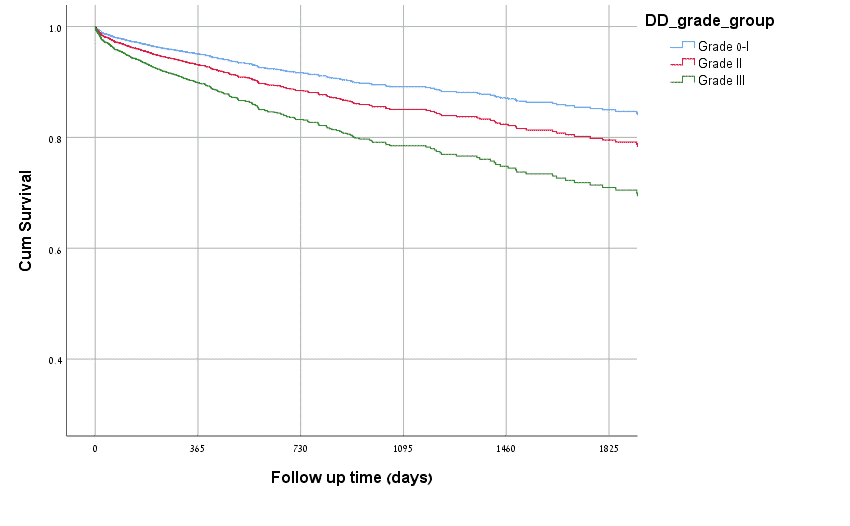
Kaplan Meier survival curve in relation to LVDD grade (Plog-rank< 0.0001):
Independent predictors for all-cause mortality [ HR, 95% CI] were: age, 1-year increment 1.07, (1.06-1.09); CHF 1.82, (1.35-2.46); Moderate-severe AS/AR/MR 1.78 (1.37-2.32); Diabetes 1.74 (1.36-2.22); LVDD-II 1.75 (1.20-2.58); LVDD-III 2.55 (1.90-3.44); Hyperlipidemia 0.64 (0.50-0.81).
Conclusions: LVDD grade II and more prominently grade III were independent predictors of all-cause mortality among hospitalized pts with normal/preserved LV systolic function. It is conceivable that treatment targeting LVDD may improve outcome.
Powered by Eventact EMS