
Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in heart transplanted Patients- a prospective cohort study
2Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel
3Department of Microbiology, Rabin Medical Center, Israel
4Department of Pulmonology, Rabin Medical Center, Israel
5Department of Infectious Diseases, Rabin Medical Center, Israel
6Department of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, Rabin Medical Center, Israel
Aims: To assess the short-term immunogenicity to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccine in a population of heart transplanted (HTx) patients.
Methods: A prospective single-center cohort study of HTx patients who received a 2-dose SARSCoV-2 mRNA vaccine (BNT162b2, Pfizer-BioNTech). Whole blood for anti-spike IgG (S-IgG) antibodies were drawn at days 21-26 and at days 35-40 after the first vaccine dose. Geometric mean titers (GMT) 50 AU/mL were considered positive.
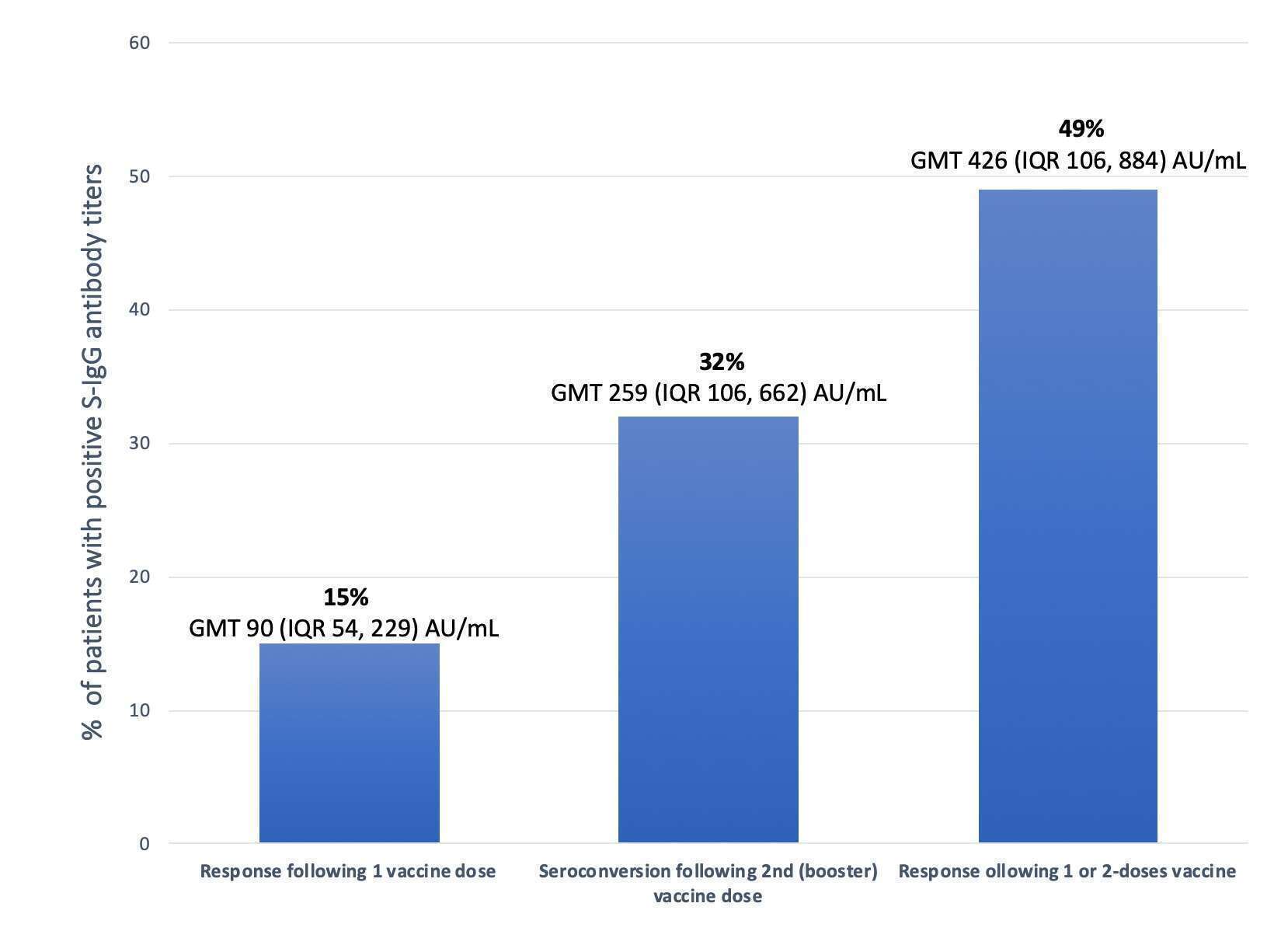
Results: Included were 42 HTx patients at a median age of 61 (IQR 44, 69) years. Median time from HTx to the 1st vaccine dose was 9.1 (IQR 2.6, 14) years. Only 15% of HTx patients demonstrated the presence of positive S-IgG antibody titers in response to the 1st vaccine dose (GMT 90 (IQR 54, 229) AU/mL). Forty-nine percent of HTx patients induced SARSCoV-2 neutralizing antibodies in response to either the 1st or 2nd vaccine doses (GMT 426 (IQR 106, 884) AU/mL). Importantly, 36% of patients became S-IgG seropositive in response to the 2nd, but not the first, vaccine dose.
Discussion: Approximately a half of HTx patients did not generate neutralizing antibodies following SARSCoV-2 2-dose vaccine. The generally achieved protection from SARS-CoV-2 attributed to the SARSCoV-2 mRNA vaccination should be regarded with caution in the population of HTx patients. The possible benefit of future booster vaccine doses based on GMT levels should be further studied.
Powered by Eventact EMS