
Low and Full Dose Apixaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Renal Dysfunction: Findings from a National Registry
2Department of Internal Medicine “C”, Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Campus, Israel
3Cardiac Rehabilitation Institute, Leviev Heart Center, Sheba Medical Center, Israel
4Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Israel
5Heart Research Follow-Up Program, University of Rochester Medical Center, USA
Background: The use of direct oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation is robust. However, the efficacy and safety of different dosage in patients with renal dysfunction is still a clinical challenge. We aimed to evaluate the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients treated with apixaban in its different doses.
Methods: A multicenter prospective cohort study, where consecutive eligible apixaban or warfarin treated patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and renal impairment (eGFR MDRD < 60 ml/min/BSA) were registered. All patients were prospectively followed-up for clinical events and dosing adjustments over a mean period of 1 year. Analyses were performed according to the dose of apixaban given, with consideration to the standard indications for dose reduction. The primary outcome was a composite of 1-year mortality, stroke or systemic embolism, major bleeding and myocardial infarction, while secondary outcomes included those components separated.
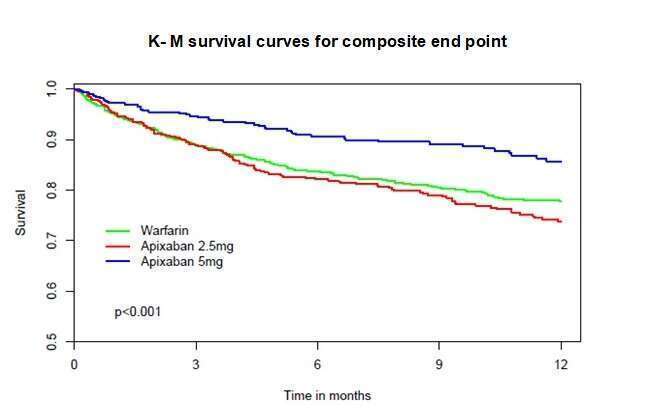
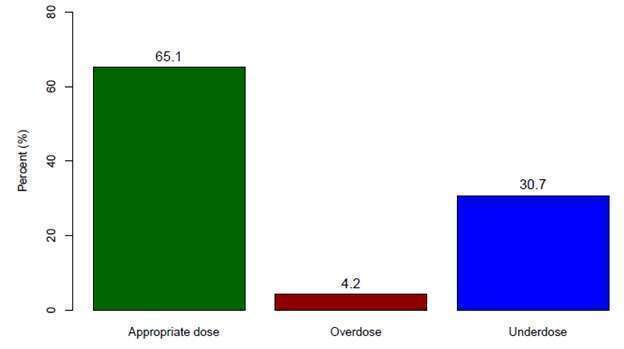
Results: Among the study population (n=2140), the risk of the composite outcome was significantly lower in the high dose apixaban group (9.6%, n=491) than the low dose group (18.3%, n= 673) and the warfarin group (18.3%, n=976) p<0.001. The results of 1-year mortality were similar. Apixaban dosing analysis revealed 65.1% of patients were appropriately dosed, while 30.7% were under-dosed and 4.2% were over-dosed. Furthermore, 53% of the patients who were treated by low dose apixaban were under-dosed. Propensity score analysis revealed that patients who were treated with low-dose apixaban had a trend towards better composite outcome and mortality than 1:1 matched warfarin treated patients. Overall, appropriately dosed apixaban treated patients (any dose) had significantly better outcomes than matched warfarin treated patients.
Conclusion: Apixaban at any dose is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with renal impairment, possibly associated with improved outcomes.
Key Words: Atrial Fibrillation; Apixaban; Warfarin; Chronic renal failure; Stroke;
Powered by Eventact EMS