
Initial experience and evaluation of a novel robotic radiation shielding device for interventional cardiology procedures
2Cardiology, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Israel
Introduction: A robotic Radiation Shielding System (RSS) was developed to provide a full-body protection to all medical personnel during fluoroscopy-guided procedures, by encapsulating the imaging beam and blocking scattered radiation. We aimed to evaluate its efficacy using a phantom model, and to perform preliminary first-in-man assessment of its clinical integration.
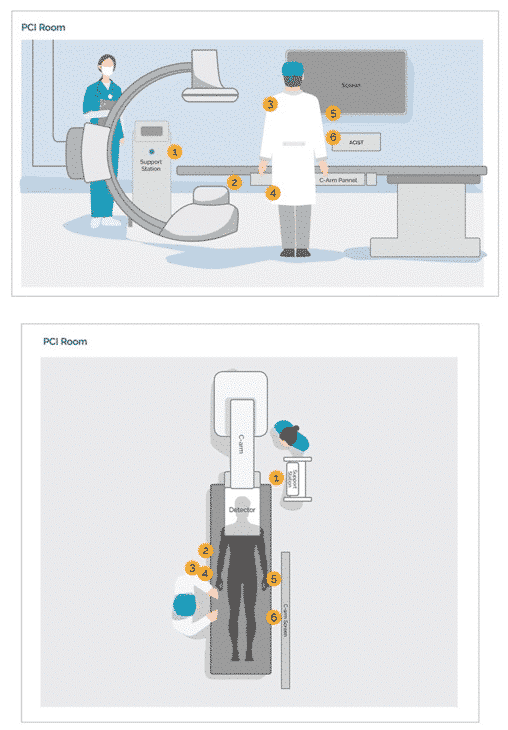
Methods and Results: We used a phantom catheterization laboratory (CL) to evaluate radiation attenuation performance profile of RSS at different locations around the C-arm relevant for CL personnel. Preliminary clinical assessment was done in coronary laboratory - radiation measurements using RSS were compared to standard protection. Bench tests showed significant radiation reduction performance with RSS- mean reduction 91.5% in all locations. For real-world-first-time clinical use of RSS, the mean radiation rate reduction for non-emergent percutaneous coronary interventions was 91.2% at different sensors (Figure 1). Total radiation time was similar with and without RSS. User`s feedback indicated high satisfaction regarding integration in clinical workflow, safety and learning curve.
Conclusions: RSS bench performance shows significant radiation reduction. Preliminary clinical evaluation shows the system is safe and highly integrated into the clinical workflow. Additional data is needed to evaluate its clinical real-time performance.
Figure 1. Sensor locations: Coronary interventions (top view and side view):
Powered by Eventact EMS