
Resectional Versus Non-Resectional Technique for Mitral Valve P2 Prolapse Repair
2Cardiology, Sheba Medical Center, Israel
Background: We investigated early and late outcomes in patients who underwent mitral valve repair (MVr) of the P2 segment using the resectional technique that included triangular or quadrangular resection with annuloplasty (group R) and compared them to patients who underwent MVr by the non-resectional technique that included artificial chordal implantation with annuloplasty (group NR).
Methods: Between 2004 and 2020, 369 patients with severe mitral regurgitation (MR) due to P2 pathology underwent MVr using either P2 resection (N=113, 31%) or artificial chordal implantation (N=256, 69%) concomitant to annuloplasty in our department.
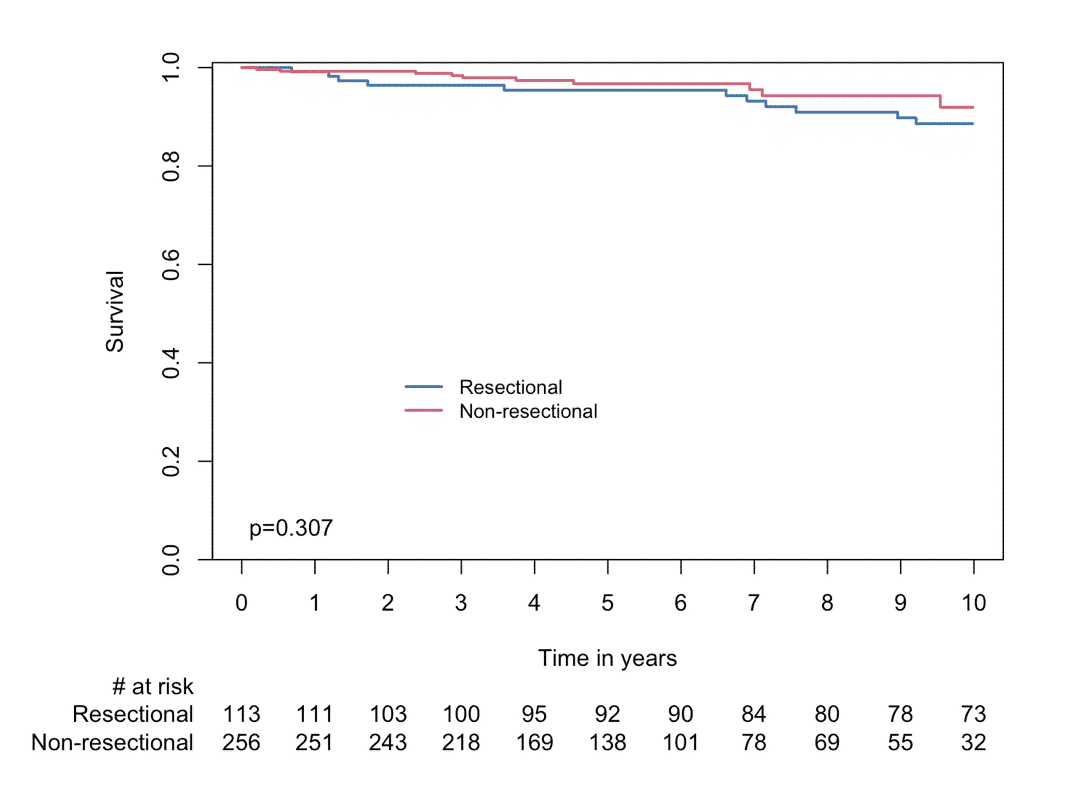
Results: There were no cases of in-hospital or 30-day mortality in the entire cohort. There was no difference in operative complications between the R and NR groups such as re-exploration for bleeding (1.8% vs. 2.3%, p=1.000), stroke (2.7% vs. 1.2%, p=0.567), permanent pacemaker implantation (1.8% vs. 0.8%, p=0.764), and sternal wound infection (1.8% vs. 0.4%, p=0.465). During a mean follow-up of 90±54 months, there were no difference in the mortality hazard between the groups (log-rank p=0.307, Figure). During this period 5 patients (4.4%) in the R group and 21 patients (8.2%) in the NR group required reoperation on the MV due to recurrent MR (p=0.277). The functional capacity was excellent in both groups (NYHA I-II 97.4% in the R group and 93.6% in the NR group, p=0.360). At the latest follow-up there were 2 patients (1.8%) in the R group, and 3 patients (1.5%) in the NR group, that had recurrent severe MR (log-rank p=0.260).
A multivariate Cox analysis using a stepwise selection process demonstrated that permanent atrial fibrillation (HR 5.29 95%CI 1.48-18.92, p=0.010) and worse pulmonary artery pressure (HR 1.05 95%CI 1.01-1.08, p=0.007) were the only predictors for recurrent moderate or more MR in this cohort.
Conclusion: Since early mortality, late functional capacity, MR recurrence, and re-operation rates did not differ significantly between the groups, either group is not preferable over the other for P2 pathology MVr.
Powered by Eventact EMS