
Impact of Pre-existing Right or Left Bundle Branch Block on Patients Undergoing Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in the Era of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
2Cardiology, Sheba Medical Center, Israel
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of pre-existing RBBB or LBBB on clinical outcomes in patients undergoing AVR, with particular focus on permanent pacemaker implantation (PPI).
Methods: Data from patients who underwent AVR surgery between 2004 and 2020 were obtained from our departmental database. Of the 2758 study patients, 206 (7.5%) had pre-existing RBBB or LBBB and 2552 (92.5%) had normal atrioventricular conduction.
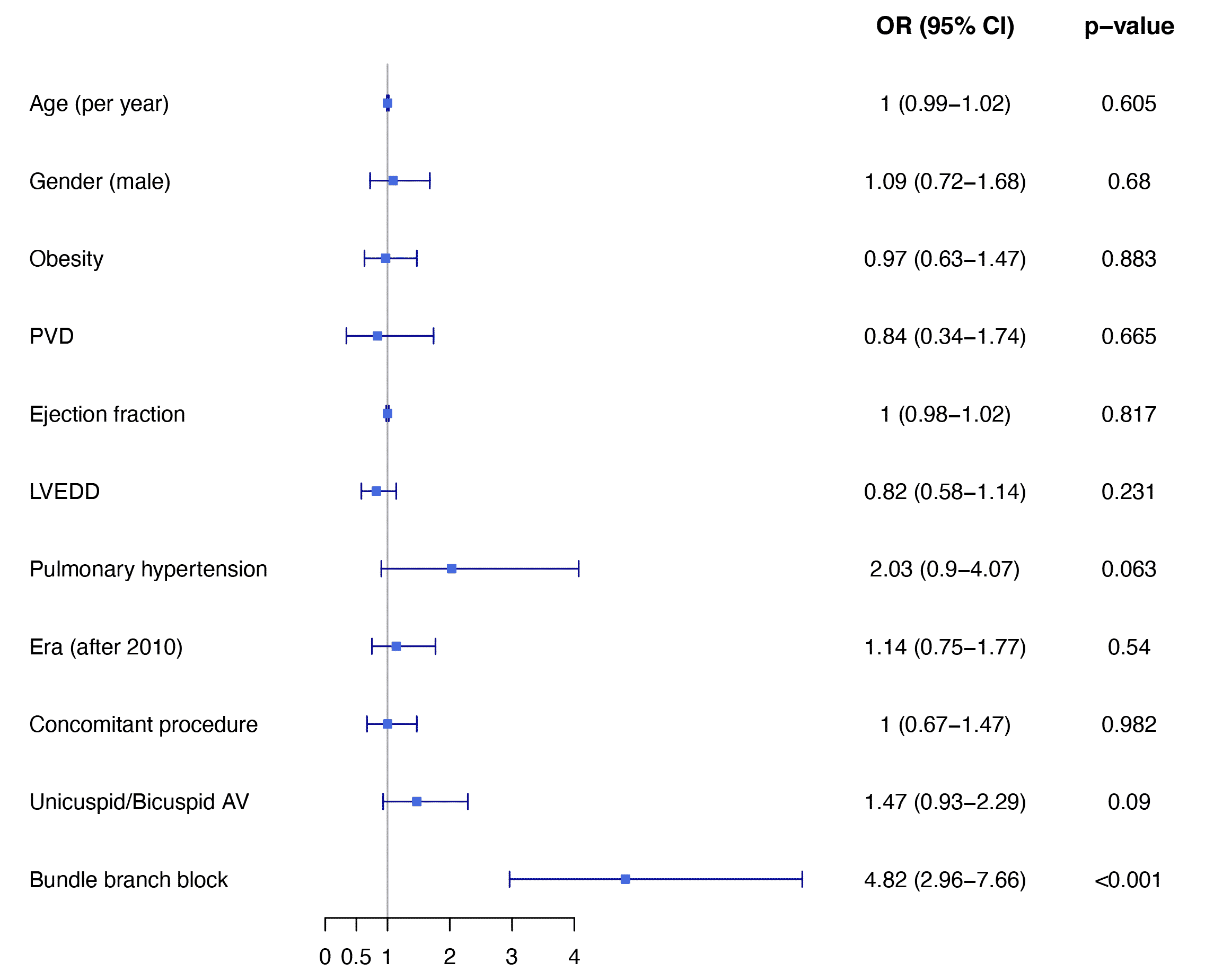
Results: Mean age was 68±13 years, 1717 (62%) were male and 695 (25%) had a unicuspid or bicuspid AV. The in-hospital mortality rate was higher in patients with pre-existing RBBB or LBBB compared to those without BBB on admission (5.8% vs. 2.9%, p=0.031), and more frequent in patients with LBBB compared with RBBB (11.9% vs. 4.3%, p=0.002). New PPI was most frequent in those patients with pre-existing LBBB, followed by RBBB and no BBB on admission (28.6% vs. 8.5% vs. 3.1% respectively, p<0.001; OR 4.82 95%CI 2.96-7.66, p<0.001) (Figure). The 10-year cumulative survival rate was lower in patients with RBBB or LBBB compared with patients with no BBB (77.2% vs. 82.9%, log-rank p<0.001; HR 0.67, CI 0.49-0.91, p=0.009).
Conclusions: This study indicates that patients with pre-existing RBBB or LBBB have a higher incidence of PPI and all-cause mortality after AVR compared with patients without a conduction disturbance.
Powered by Eventact EMS