
The feasibility of Transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis scintigraphy using planar D-SPECT on dedicated cardiac CZT camera
Background Scintigraphy is a main diagnostic tool in suspected ATTR patients. Almost all literature is based on conventional whole body gamma cameras, and the use of dedicated cardiac CZT cameras has not been described. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of planar D-SPECT scintigraphy on a dedicated cardiac CZT camera in suspected transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR-CA) patients.
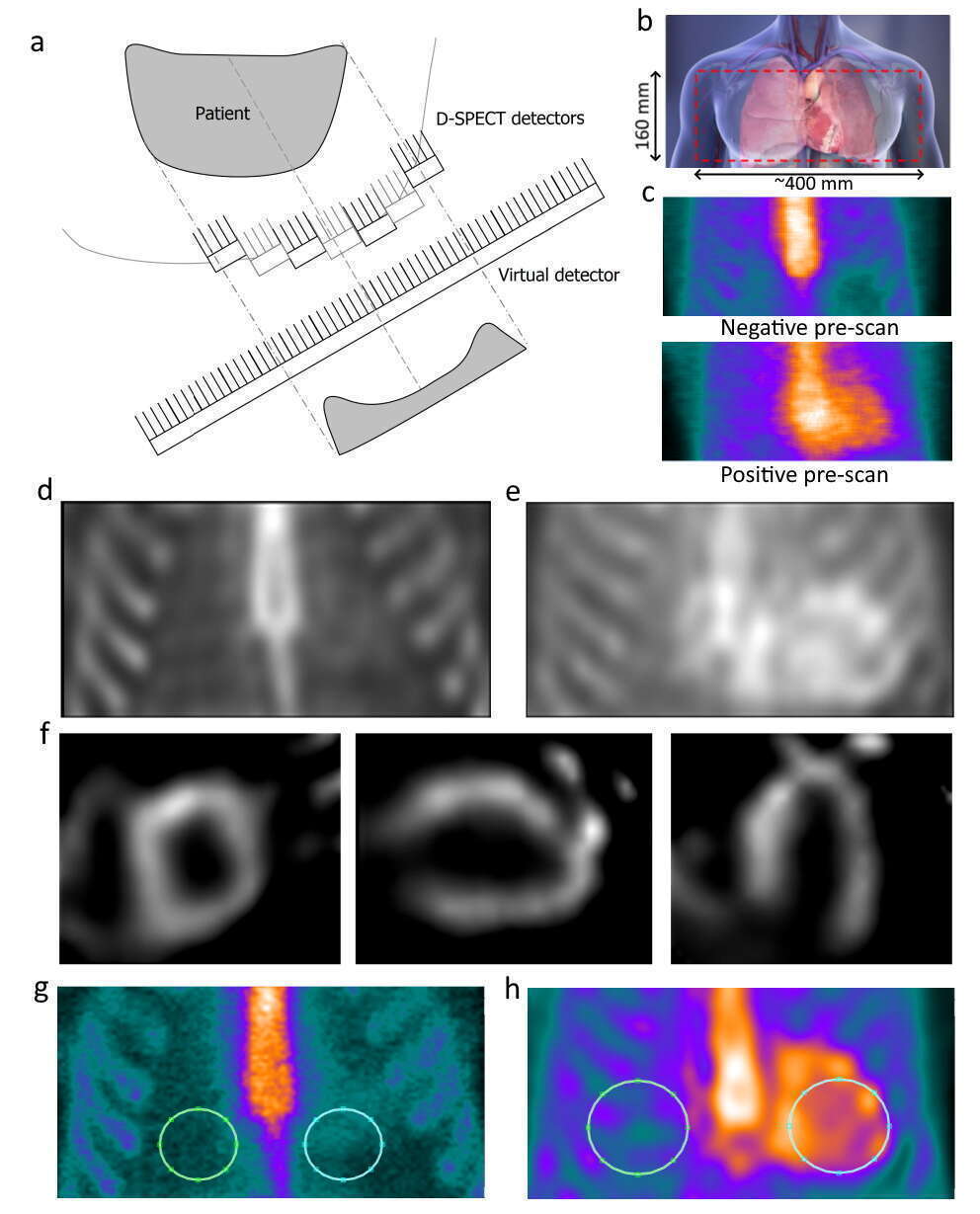
Methods Seventy three patients with suspected ATTR-CA underwent planar and SPECT Tc-99m pyrophosphate scintigraphy using dedicated cardiac CZT camera between May and August 2019. The D-SPECT camera incorporates 9 swiveling CZT detectors, which using the manufacturer`s protocol can be aligned in the same direction to create a true planar image. Two independent observers evaluated all cases using Perugini score, and heart to contralateral ratio (H/CL) was calculated using a Matlab H/CL calculation tool.
Results Planar D-SPECT image quality was mostly good. Six patients were identified as ATTR-CA positive and 67 patients were identified as negative. Inter-observer agreement based on both Perugini score (ICC 0.940; 95% CI 0.906-0.963; p<.001) and on planar D-SPECT H/CL ratio (ICC 0.930; 95% CI 0.888-0.956; p<.001) was excellent.
Conclusions ATTR-CA scintigraphy using dedicated cardiac CZT camera was feasible, and yielded planar D-SPECT images with excellent inter-observer agreement.
Powered by Eventact EMS