
Guidelines endorsed parameters for the Prediction of outcome following functional mitral regurgitation edge-to-edge mitral valve repair
2The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine in the Galilee, Bar-Ilan University, Israel
Introduction
The optimal criteria for defining secondary MR (SMR) severity are controversial with two major cardiology societies using different staging criteria. Furthermore, there is a continuing debate regarding the criteria for invasive management of severe SMR by either surgery or transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER). The aim of this analysis was to assess whether in SMR patients who underwent TEER, the aforementioned criteria would be associated with improved clinical course.
Materials and Methods
We analyzed data of FMR patients from Padeh medical center prospective TEER registry. Univariable and multivariable cox regression analyses were applied on demographic, medical background, clinical and echocardiographic parameters. The end-point was the composite of time to mortality and/or first heart failure hospitalization
Results and Discussion
Between October 2015 and December 2020, 58patients with SMR have undergone TEER at Poriya medical center. Their mean age was 75±6.8, and 33 (57%) were males. 46 (79%) had concomitant coronary artery disease (CAD) and 36 (62%) had history of myocardial infarction (MI).
The univariable analysis indicated that, past MI was significantly associated with the composite end-point (HR 2.732, 95% CI 1.105-6.755, P=0.03) as did diabetes mellitus (DM) (HR 2.691 95% CI 1.497-4.873, p=0.001), regurgitant volume ≥60 ml (HR 2.461 95% CI 1.096-5.528, p=0.029) and Left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) of 20% to 50%. (HR 4.693 95% CI 1.337-16.474, p=0.016).
The multivariable analysis indicated that DM (HR 3.781, 95% CI 1.756-8.143; p=0.001), Past MI (HR 3.458, 95% CI 1.206-9.916; p=0.021) and Regurgitant Volume≥60ml (HR 2.85, 95% CI 1.184-6.857; p=0.019) remained predictive of the end-point.
Conclusions
Regurgitant volume of ≥60 ml, according to this analysis, is associated with worst clinical outcome following TEER. This variable may imply advance stage of cardiac remodeling associated with FMR, which may have contributed to the poorer results in these patients. This finding needs further validation and investigation.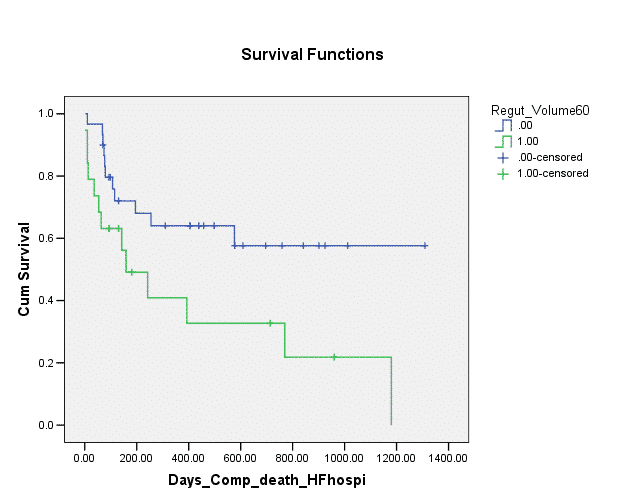
Powered by Eventact EMS