
Theranostic targeted drug delivery – new insights into diagnosis and treatment of cancer
2Molecular Biology, Ariel University, Israel
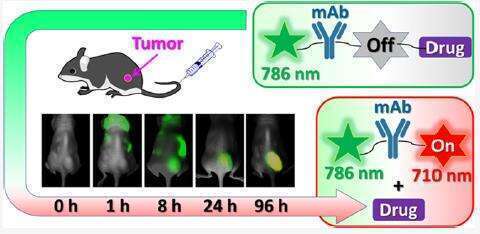
Fluorescent dyes linked to drug delivery systems provide important real-time information on the efficacy of drug delivery. However, the quantitative monitoring of drug distribution is challenging because of interferences from the biological sample and instrumental setup. To improve quantification of anticancer drug delivery followed by drug release in tumor, we equipped an antibody−drug conjugate (ADC) with a turn-on near-infrared (NIR) dye, sensitive to drug release, and a reference NIR dye. In this study, chlorambucil (CLB) was chosen as a model anticancer drug and Trastuzumab monoclonal antibody specific to Her2 receptors overexpressed in many tumors was taken as the carrier. The advantage of the dual-dye ratiometric system for drug release monitoring was demonstrated in Her2-positive BT-474 tumor mice model. The results suggest that our ratiometric design could be successfully employed for quantitative monitoring of drug release degree and the proposed method is unaffected by the experimental variation, as well as the variation in the mouse response to the administrated conjugate.
1. Thankarajan E., Jadhav S., Luboshits G., Gellerman G., Patsenker L. Analytical Chemistry 2021 93 (23), 8265-8272; DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c01104.
2. Rozovsky, A., Ebaston, T. M., Zaporozhets, A., Bazylevich, A., Tuchinsky, H., Patsenker, L., Gellerman, G. Theranostic system for ratiometric fluorescence monitoring of peptide-guided targeted drug delivery. RSC Advances 2019, 9(56), 32656–32664. doi:10.1039/c9ra06334j.
Powered by Eventact EMS