
TUNABLE MIE RESONANCE IN BAR- AND CUBE-LIKE GADOLINIUM NIOBATE: THEORY AND EXPERIMENT
2Department of Physics, Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN, Ciudad de México, Mexico
3Department of Chemistry, Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN, Ciudad de México, Mexico
Submicron particles described by Mie resonance in the UV-Vis-NIR region are in high demand for designing lasing and luminescence enhanced systems.1,2 The ability to control the shape and the size of the particles is essential as it results in an ability to control the location of the Mie resonance peak.3 Among the studied materials, all-dielectrics are the center of attention given their versatility and ability to overcome limitations such as energy dissipation and absorption that are present in metallic nanoparticles.4 In this work, we study the Mie resonance in the UV-Vis-NIR region in gadolinium niobate with bar- and cube-like morphologies. We perform our experimental analysis by characterizing the morphology and the extinction spectra using scanning electron microscopy and a spectrophotometer, respectively, and our theoretical study by implementing a simple model of spherical particles. With this, we model with high accuracy the size distribution and the extinction spectra. We calculate the contribution to the Mie scattering of the dipole, quadrupole, and octopole and their respective electric and magnetic parts. Our results demonstrate that the broad Mie resonance peak in the extinction spectra can be tuned by the nanoscale characteristics of the system under consideration. These dielectric gadolinium niobate submicron particles are great candidates for light manipulation in the nanoscale.
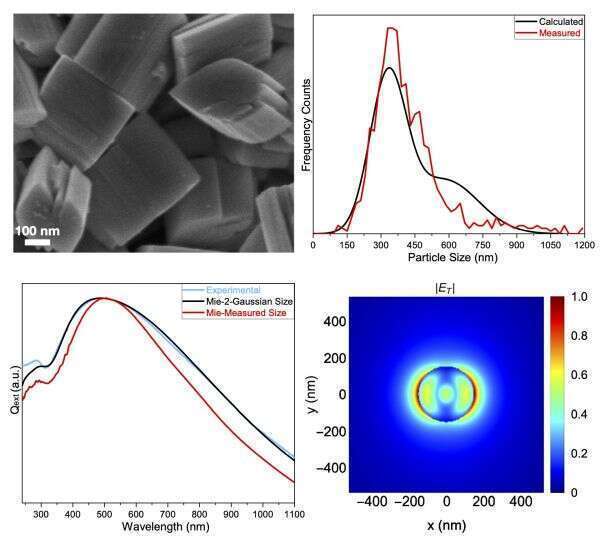
Figure 1. Morphology, calculated and experimental extinction and size distribution spectra, and near field calculation.
References:
(1) Tiguntseva, E.; Koshelev, K.; Furasova, A.; Tonkaev, P.; Mikhailovskii, V.; Ushakova, E. V; Baranov, D. G.; Shegai, T.; Zakhidov, A. A.; Kivshar, Y. Room-Temperature Lasing from Mie-Resonant Nonplasmonic Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2020, 14 (7), 8149–8156.
(2) Tiguntseva, E. Y.; Zograf, G. P.; Komissarenko, F. E.; Zuev, D. A.; Zakhidov, A. A.; Makarov, S. V; Kivshar, Y. S. Light-Emitting Halide Perovskite Nanoantennas. Nano Lett. 2018, 18 (2), 1185–1190.
(3) Yadgarov, L.; Choi, C. L.; Sedova, A.; Cohen, A.; Rosentsveig, R.; Bar-Elli, O.; Oron, D.; Dai, H.; Tenne, R. Dependence of the Absorption and Optical Surface Plasmon Scattering of MoS2 Nanoparticles on Aspect Ratio, Size, and Media. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3575–3583.
(4) Jahani, S.; Jacob, Z. All-Dielectric Metamaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11 (1), 23–36.