
Bias-free photoelectrochemical water-splitting using epitaxial (Pb,La)TiO3 thin films
2College of Science and Engineering, Tokyo Denki University, Hatoyama, Japan
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is known to be an effective method for H2 production. For practical usages, however, it is desirable that the PEC cells are operated under a bias-free condition which does not require any consumption of additional energy. Since a few years ago, investigations on ferroelectric materials have been conducted because they inherently possess internal electric fields. (Pb,La)TiO3 (PLT) is a renowned material because of its good ferroelectric characteristics. We deposited c-axis oriented epitaxial-PLT thin films on platinized MgO001 (PLT/Pt/MgO). From above, photocathodic responses were verified, and specifically, quite large photopotential (Vph) of more than 2.42 V were observed. The Vph is attributed to a highly stabilized polarization in the PLT, and the value was sufficiently larger than the potential required for water splitting (1.23 V + overpotential, η). It enabled the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) under bias-free conditions.
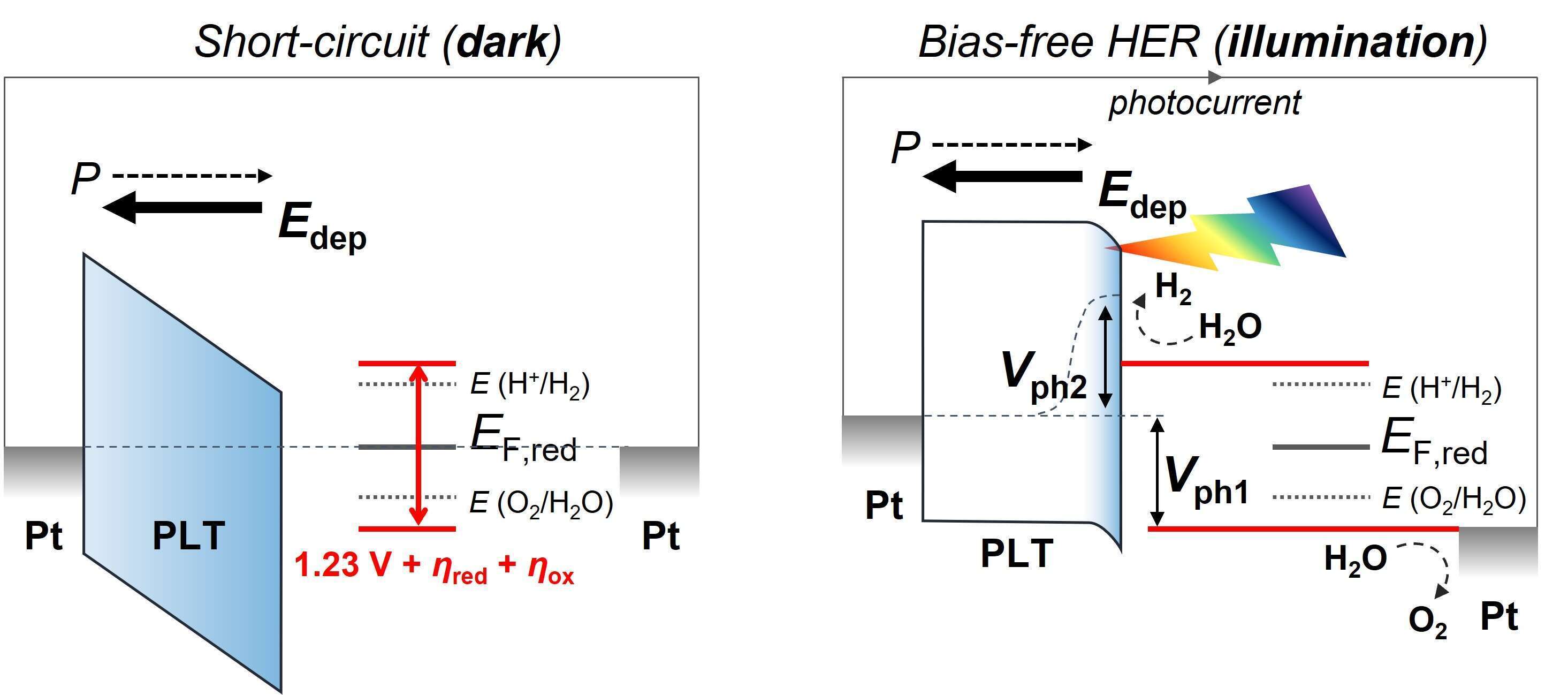
Fig. Schematics for a photocathode including an epitaxial PLT thin film as a photoactive material at an equilibrium state (left) and under a sufficient illumination (right).
Powered by Eventact EMS
