
Fabrication and characterization of epitaxial PZT thin films on Si substrates by sol-gel process
2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kobe University, Kobe, Japan
Sol–gel process is a popular deposition method for achieving stoichiometric composition control and large area thin-film fabrication at low cost [1]. Recently, several studies have demonstrated the fabrication of epitaxial Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 (PZT) thin films on Si substrates with buffer layers by the sol–gel process [2]. Although epitaxial growth of the PZT thin films by sol-gel process has already been reported, these studies mainly focused on their crystal structure and electrical properties without detailed piezoelectric characteristics.
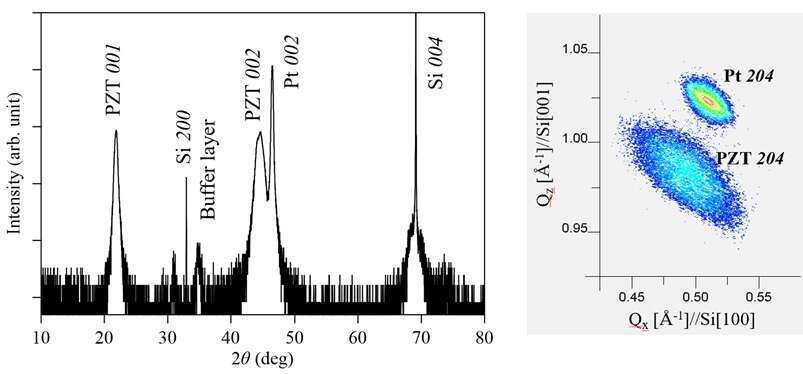
In this study, we compared the piezoelectric properties between c-axis oriented epitaxial and randomly-oriented polycrystalline PZT thin films on Si deposited by the sol–gel process. X-ray diffraction measurements revealed a cube-on-cube epitaxy on the ZrO2-buffered Si substrate (Fig. 1). We found the |e31,f | values from the converse piezoelectric effect were in the range of 8.9–12 C/m2, comparable to the epitaxial PZT obtained by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. The epitaxial sol–gel PZT thin films thus exhibited good piezoelectric properties for applications in microelectromechanical systems devices. We will report our comparison study between epitaxial and polycrystalline PZT thin films in the meeting.
[1] K. Ueda, S.H. Kweon, H. Hida, Y. Mukouyama, I. Kanno, Transparent piezoelectric thin-film devices: Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 thin films on glass substrates, Sensors Actuators, A Phys. 327 (2021) 112786.
[2] R. Moalla, B. Vilquin, G. Saint-Girons, G. Sebald, N. Baboux, R. Bachelet, Dramatic effect of thermal expansion mismatch on the structural, dielectric, ferroelectric and pyroelectric properties of low-cost epitaxial PZT films on SrTiO3 and Si, CrystEngComm. 18 (2016) 1887–1891
Powered by Eventact EMS
