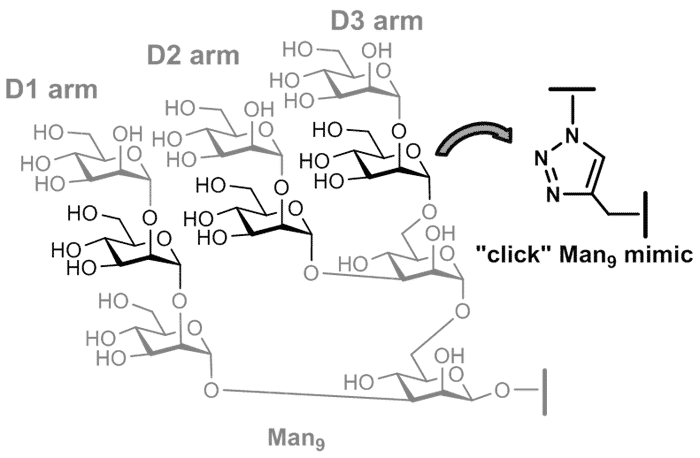
« High-mannose » type N-glycans
are well known to participate in quality control and intracellular traffic of
glycoproteins. They cover the surface of many pathogenic microorganisms and are
the targets of the immune system cells through their mannose receptors.
Several groups have reported the synthesis of such complex structures
but it remains very cumbersome and costly. Their uses as carbohydrates-based
vaccines[1] and as recognition
moieties in drug delivery[2] or
in antigen targeting to dendritic cells[3]
have also been investigated.
In the pursuing of our work to investigate the recognition
phenomena of “high-mannose” type oligosaccharides with lectins,[4] we undertook to design “high-mannose” mimics that retain as much as possible the three-dimensional structure of the native molecule. The synthesis of octa[5] and nona-oligomannosides
mimics by replacing three mannose units with triazoles using "click chemistry" will be presented and discussed
as well. The efficiency of the Man8
mimic to inhibit concanavalin A binding to yeast mannan (IC50 = 12 µM) will be compared to its natural analogues (IC50 = 5, 17µM for Man8 and Man7, respectively). Preliminary
results of Concanavalin A / Mimics recognition studies based on Mass
spectrometry (ESI-MS) will also be presented.
[1] Mandal, M.; Dudkin, V. Y.; Geng, X.; Danishefsky, S. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2557.
[2] Becker, B.; Furneaux, R. H.; Reck, F.; Zubkov, O. A. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 315, 148.
[3] Adams, E. W.; Ratner, D. M.; Seeberger, P. H.; Hacohen, N. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 294.
[4] Smiljanic, N.; Yockot, D.; Cendret, V.; François-Heude, M.; Moreau, V.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. In Carbohydr. Chem.; The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2012; pp. 374.
[5] Cendret, V.; François-Heude, M.; Mendez-Ardoy, A.; Moreau, V.; García-Fernández, J. M.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3733.

