Glycosylation is one of the
most common post-translational modifications and influences the function of
glycoproteins in many ways. In particular, L‑fucose
is important for cell-cell interactions, regulation of protein function and for
many developmental processes.[1] This is why investigation of
fucosylated glycans is of great interest. A promising approach to visualize
glycoconjugates is metabolic oligosaccharide engineering (MOE) that allows to
monitor glycans by using a chemical ligation reaction.
Recently, we could show that
terminal alkenes can be successfully used in a Diels-Alder reaction with
inverse electron demand (DARinv) with a tetrazine to label cell-surface sialic
acids.[2] The advantage of terminal alkenes is that they are small
and thus accepted by metabolic processes. Moreover, the DARinv has been shown
to be bioorthogonal as well as orthogonal to click chemistry and therefore is
suitable for dual labeling.[2]
C6-modified fucose
derivatives are known to be accepted by the fucose salvage pathway and
incorporated into fucosylated glycanes.[1,3] Here we show the
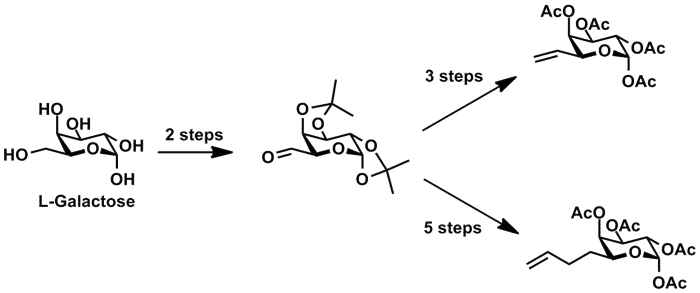
synthesis of two L-fucose
derivatives bearing terminal alkenes at the C6 position for use in MOE. Starting
from aldehyde 1, which is available
in two steps from L-galactose,
sugars 2 und 3 were prepared in three and five steps, respectively.
[1] D. Rabuka, S. C.
Hubbard, S. T. Laughlin, S. P. Argade and C. R. Bertozzi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12078-12079.
[2] A. Niederwieser, Späte, A.-K.,Nguyen, L.D., Jüngst, C.,
Reutter, W., Wittmann, V., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, in press.
[3] M.
Sawa, T.-L. Hsu, T. Itoh, M. Sugiyama, S. R. Hanson, P. K. Vogt and C.-H. Wong,
PNAS 2006, 103, 12371-12376.

