Introduction: Functional mitral regurgitation (MR) is a common finding in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and is defined by the presence of MR with a structurally normal valve. Under contemporary therapies, reverse remodeling (RR) is a well recognized phenomenon in some DCM patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the mechanism of MR improvement after RR.
Methods: We evaluated 10 DCM patients who qualified as RR and reduced their MR severity by ≥ 2 grades (group1). Their baseline examinations were compared to their echo-Doppler after improvement. A similar comparison was obtained in a control group of 10 DCM patients with similar LV dysfunction and MR severity at baseline, who did not improve their function or MR during follow-up( group2) .LV and LA dimensions , LV end-systolic(LVESV) and end- diastolic volumes(LVEDV) ,LV Mass, LVMi, LVEF (Simpsons), sphericity index(SI) , mitral valve tenting area(TA) and coaptation distance(CD) were measured. MR was quantitatively evaluated (PISA) and the effective regurgitant orifice (ERO) calculated.
Results: Baseline clinical characteristics including age, gender, BSA, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, renal failure and medical treatment were similar between the groups. Group 1 had a significantly bigger baseline LA diameter, LV systolic and diastolic dimensions, LVM, LVMi, LVESV,LVEDV, SI LVEF,ERO, TA and CD compared to follow- up (Table 1). Compared to group 2, group 1 had a similar ERO (0.2 vs 0.24, p=0.13), higher LVEF(28±10 vs 21±4%)but significantly smaller LA(42±4 vs 49±5 mm) and LV dimensions(57±2 vs 67±9 mm), LVESV(98±34 vs 150±55 cm3), LVEDV(135±37 vs 188±61 cm3), LVM(231±38 vs 318±121 g), LVMi(124 ±15 vs 177±78 g/m2 and SI(0.56±0.07 vs 0.66±0.05) (all p<0.05).
Conclusions: Functional MR decrease in the course of RR is related to reduction in the chamber size and improvement in LV function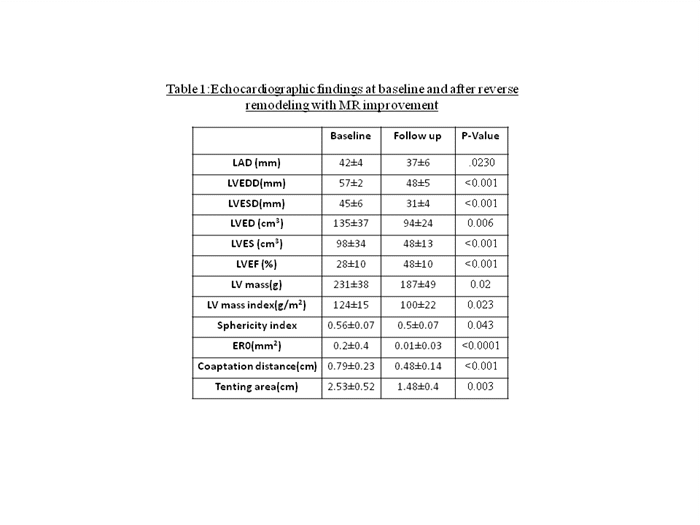 .
.

