Background: Cardiac CT is mainly used to assess coronary anatomy while it can also evaluate cardiac function. However there is a need for a sensitive quantitative parameter of regional myocardial function.
Aim: To develop and test a method that calculates regional myocardial strains and twist from cardiac CT image data.
Method: We developed an automatic finite element based tracking algorithm that utilizes the trabeculae and papillary muscle texture in the framework of a functional model of the left
ventricle (LV). This deformed LV mesh model consists of the myocardial and blood
pool regions with their different material properties. This geometric material separation
accounts for the elasticity and incompressibility of the myocardium with the rapid contraction of the blood pool. Fourty-two patients (22 normal, 20 abnormal) underwent CT - 17 also had speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) analysis within one month. We compared the algorithm’s strain and rotation to STE analysis and against visual scores.
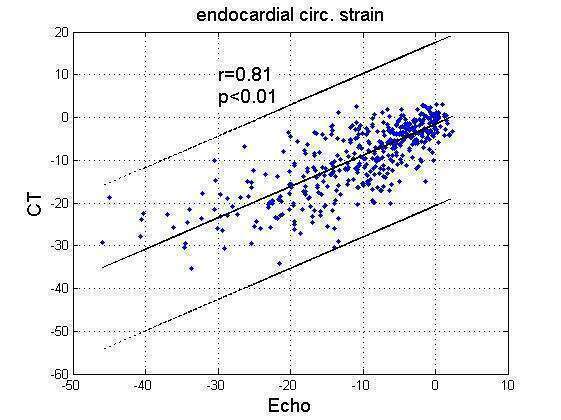
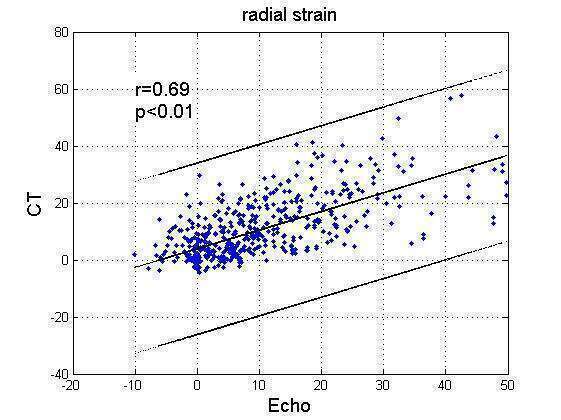
Results: CT based and STE-based circumferential (Scirc) and radial (Srad) strains, per territory, correlated well (r=0.81 and r=0.69, p=0.01, Figures 1 & 2). CT and STE twist angles correlated moderately (r=0.5, p=0.01). By Bland-Altman analysis, CT overestimated circumferential strain by 0.7± 10.4 and overestimated radial strain by 1 ± 16.5.
With respect to the expert’s visual scores, Scirc was- 25.2±7.8,-17.2±7.0 and -11.1± 8.5 (p=0.01), and Srad, 30.3 ± 12.5, 17.2 ± 7.0, and 13.9 ± 11 (p=0.01) for the normal, hypokinetic and akinetic regions, respectively. Receiver-operating-characteristic analysis for Scirc and Srad to differentiate between normal and abnormal visual segments gave AUC=0.83 and 0.82, respectively. Sensitivity = specificity was 75% for Scirc at a threshold of 21.7 and 76% at a threshold of 19.5 for Srad.
Conclusions: Our study shows for the first time that circumferential and radial strains from Cardiac CT image data can be used in clinical practice for automatic quantitative assessment of regional myocardial function.