Pneumonia exhibits a broad range of severity ; it is claimed that clinicians could reliably diagnose pneumonia by Thoracic UltraSound (TUS). We re-assessed in how many patients we were able to confirm by TUS the clinical and Chest-XRay (CXR) diagnosis of pneumonitis. After a preliminary CXR diagnosis, areas of consolidation were identified by TUS in 288/375 children and in 512/645 adults, i.e. about 80%. By monitoring lung consolidations in adults modifications were: initial dimensions cm. 3.5-9.5 (6.3±3.4), intermediate dimensions cm. 2.1-4.3 (2.5±1.8); final dimensions cm. 0.3-1.0 (0.9±1.4);p<0.001. By monitoring lung consolidations in children modifications were: initial dimensions cm. 2.5-4.5 (3.4±1.7), intermediate dimensions cm. 1.8-2.6 (1.1±0.8); final dimensions cm. 0.26-0.75 (0.2±0.5); p<0.001. Even if TUS appears a reliable substitute of CXR useful for follow-up, most pneumonitis, at least 20%, that would have skipped diagnosis if trusting only on TUS, were actually detectable only by CXR and, more important, occurred also in more severely ill and at risk patients. A great care is needed for avoiding inappropriate self-confidence in the procedure, especially because it was claimed that TUS can contribute to reducing length of stay and need of radiological procedures, which is particularly relevant in pregnancy. This procedures and its interpretation imply pitfalls if used as a stand-alone tool, analogous to drawbacks occurring with artifacts: its use as a primary diagnostic tool, and not only as a complementary and monitoring procedure in pneumonitis, particularly in emergency, should be discouraged due to possible misdiagnosis and to consequent legal implications.
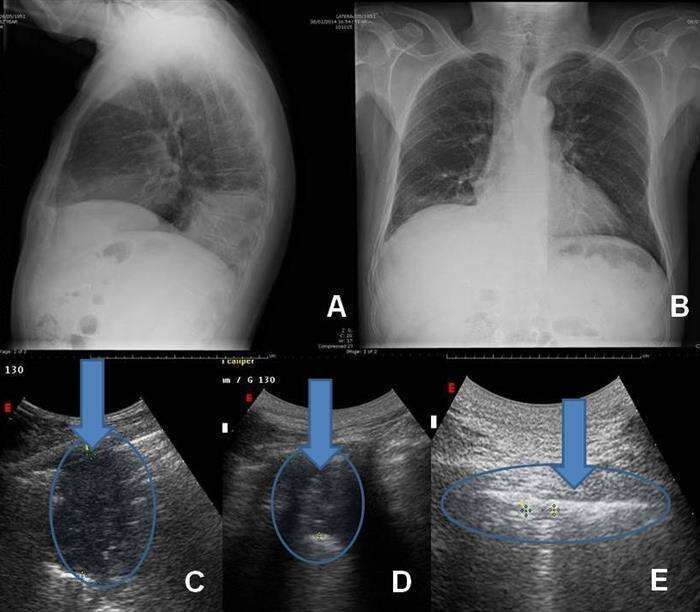
A & B) Chest X-Ray showing right-basal pulmonary consolidation. C) TUS, same day: sub-pleural consolidation (lenght 8.5 cm). D) TUS, same patient, 5 day after therapy; subpleural consolidation reduced to 3.0 cm (arrow), with a concurrent clinical improvement. E) TUS control after 11 days: disappearance of lung density; arrow indicates pleural thickening (8mm) which are a meta-neumonitis outcome.

