AIM: Medullary sponge kidney (MSK) also known as Lenarduzzi-Cacchi–Ricci disease is a renal malformation characterized by cystic dilatation of the collecting tubules in one or both kidneys, an increased risk of kidney stones,nephrocalcinosis and urinary tract infections. The frequency in general population is low, 0,02-0,005% but in patients with urinary lithiasis it can be up to 20%. The principal method of diagnosis is intravenous urography (IVU), but in asymptomatic patiens, ultrasonography has specific features.
METHOD: In a period of five months we examined 6 patients with MSK. Diagnosis was made by the ultrasound findings. Caracterisation
of the patients: two women-one being pregnant and four men, two of them being brothers with urinary stone eliminations. Patients were all under the age of 35. They were examined with an MyLab™50 XVision ultrasound machine, and GE Voluson 730.
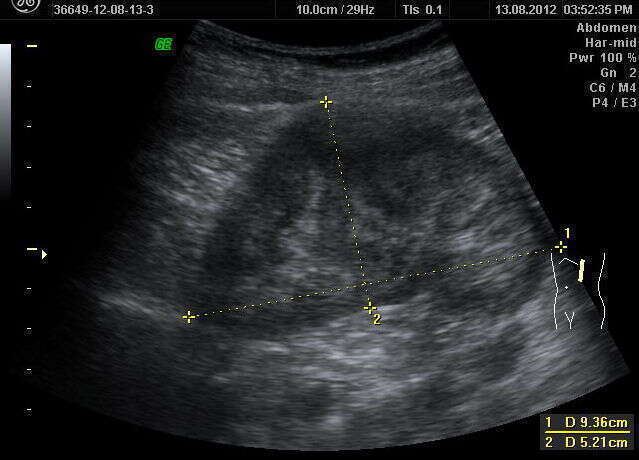
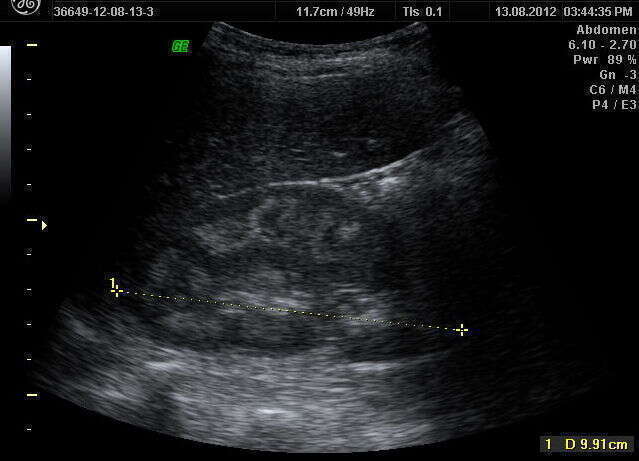
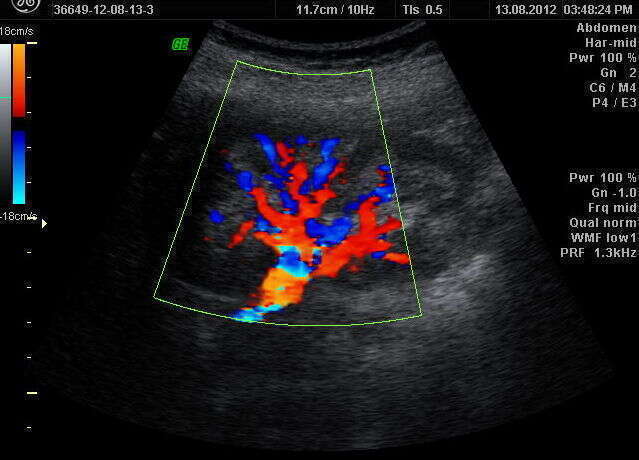
RESULTS: Ultrasound findings were: increased medullary echogenicity of both kidneys, especially in the periphery of the medulla, two cases presenting also multiple calcification within the medulla and acustic shadowing suggesting nephrocalcinosis. Doppler examination of the intrarenal arteries revealed normal parameters. In two cases, ultrasound was performed for hematuria and urinary stone elimination. IVU findings were not relevant for the diagnosis. After one year of follow up, all patients were without complications. The newborn had no signs of renal involvement and remained in pediatric observation. Differential diagnosis had to be made on
clinical basis in order to exclude other conditions with hyperechoic medulla: hyperuricemia, hypokalemia,gout, Sjogren syndrome,
primary aldosteronism, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, hyperparathyroidism, glycogen storage disease, Wilson disease, and pseudo-Bartter syndrome.
CONCLUSIONS: Although IVU is considered to be the first diagnosis line in MSK, it cannot describe the morphology of the medulla as well as the ultrasound findings, considered to be pathognomonic in this disease.