Knowledge of bubble-particle interaction is important in many industrial processes such as in flotation. While the collision (first interaction sub-process) between bubbles and particles is influenced only by hydrodynamic forces, the bubble behaviour during the attachment (second sub-process) is influenced both by hydrodynamic and surface forces. This work is focused on the study of the three-phase contact (TPC) line expansion during bubble adhesion on hydrophobic surface and on its experimental and mathematical description. The experiments were carried out in aqueous solutions of surface active agents. Influence of different type and size of surfactants (anionic SDS, cationic DTAB, non-ionic Triton and Terpineol) was compared with data obtained for pure water. The attachment process was recorded using a high-speed digital camera and diameter of TPC line as well as the dynamic contact angle were determined. Altogether the dynamic surface tension was measured. The molecular-kinetic model was used for mathematical description of the TPC line expansion.
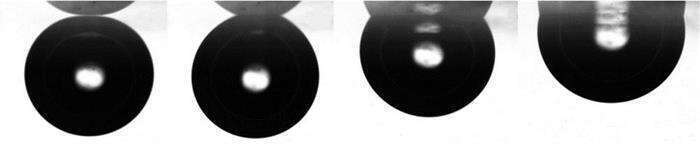
Fig. 1 Bubble adhesion onto the hydrophobic solid surface
pavlina.basarova@vscht.cz