Tuning magnetic properties is a challenge in advanced materials research, for various applications including high storage capacity media, diagnostics, imaging, hyperthermia probes or targeted delivery. Most of magnetic systems consist of either molecular nanomagnets (n < 30 atoms) or magnetic nanoparticles (n= 100-1000). Very recently, colloidal systems (i.e. micelles, micro-emulsions and emulsions), based on magneto-responsive surfactants were reported as being able to bridge this gap, allowing thus fine control upon the cluster size n, whilst combining magnetic ordering with low-density and electrical insulation [1]. Herein will be presented novel contributions on magnetic surfactants that are able to form either vesicles or solid lipid nanoparticles. Straightforward applications of these systems might be found in magneto-responsive drug delivery. Moreover, hexagonally ordered meso- and meso-macroporous materials with magnetic properties could be achieved by using magnetic surfactants as structure directing agents of silica [2]. Finally, it will be shown that magnetic properties of the self-assembled surfactants and of the resulting materials are highly dependent on the molecular organization system and on confinement of the metallic centres, respectively.
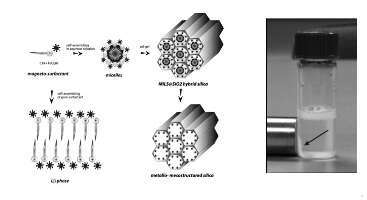
Figure 1: Imprinting pathway with magneto-surfactants of magneto-responsive porous silica
Acknowledgements: COST network CM1101 for financially supporting the STSM of Andreea Pasc to the University of Bristol (Prof. Eastoe’s group).
[1] P. Brown, A. Bushmelev, C. P. Butts, J. Cheng, J. Eastoe, I. Grillo, R. K. Heenan, A. M. Schmidt, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2414.
[2] S. Kim , C. Bellouard, A. Pasc, E. Lamouroux, J.L. Blin, C. Carteret, Y. Fort, M. Emo, P. Durand, M.J. Stébé,
J. Mater. Chem. C. 2013, 1, 6930.
andreea.pasc@univ-lorraine.fr