One way to increase the bioavailability and thus the efficiency of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is to appropriately formulate it into a vector. Nowadays challenges in encapsulation technologies for drug delivery applications are the design of nanomatrices that (i) are able to provide sustainable release of poorly soluble drugs in the receiving phase and (ii) respond to changes to external stimuli (i.e. temperature, pH). Here we report an original nano-vector by combining solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) with nano-structured silica materials, for loading and release of curcumin (CU), a hydrophobic API, bearing anti-oxidant and anti-cancer activity. The carrier matrix were prepared by first loading the curcumin into dispersions of SLN in a micellar phase, followed by the silicalization of the colloidal system by sol-gel. [1,2]. The dual templating mechanism afforded a compartmentalized nanovector, with both macro and mesostructured domains. The SLN act as a reservoir of CU while the surfactant present in mesopores is assisting the release (Fig. 1). Moreover, the sustainability of the release depends on the nature of the solid lipid and on the pH of the receiving phase. Cell viability experiments confirm the potentiality of the designed silica-SLN-CU nanovector for drug delivery formulation.
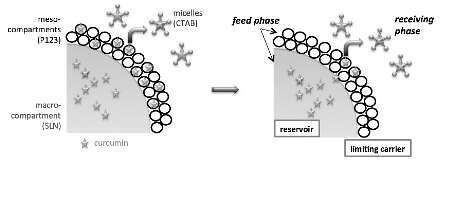
Figure 1: Surfactant-assisted and pH-controlled delivery of cur cumin from compartmentalized meso-macrostructured silica matrix
[1] Ravetti-Duran, R.; Blin, J.-L.; Stébé, M.-J.; Castel, C.; Pasc, A., J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21540-21548.
[2] Pasc, A.; Blin, J.-L.; Stébé, M.-J.; Ghanbaja, J., RSC Advances 2011, 1, 1204-1206.
andreea.pasc@univ-lorraine.fr