In the last decades the use of nanoparticles (NPs) for biomedical applications has attracted a growing research interest, promoting NPs use in imaging, therapy, and drug delivery. [1] The possibility of combining diagnostic and therapeutic properties in unique nano-objects has led to the development of new theranostic systems, [2] which might improve the prognosis of many diseases. At the same time, fluorinated tracers represent a powerful diagnostic tool for in vivo imaging through 19F MRI detection. [3] Thus, the use of fluorinated ligands for NPs surface functionalization can bring to the development of innovative theranostic agents to be employed in nanomedicine.
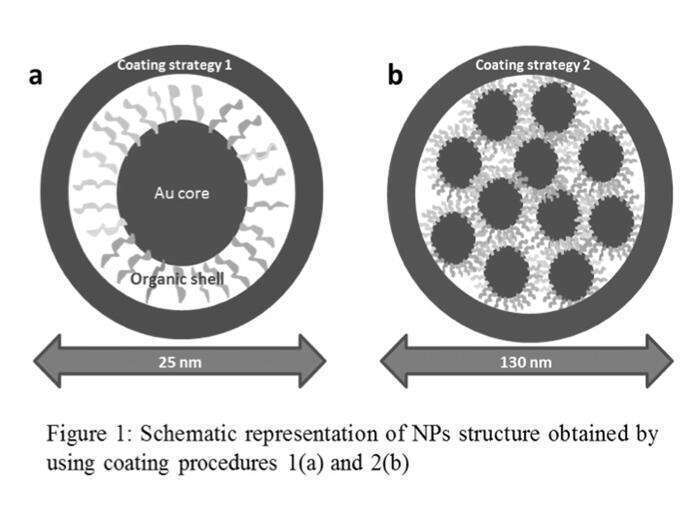
In this contribution we report on a novel multifunctional nanomaterial based on gold NPs stabilized with highly fluorinated chains or with a mixture of hydrogenated and highly fluorinated ligands. These NPs were successfully transferred into an aqueous environment using two different coating amphiphilic polymers. The obtained nanodispersions were characterized by DLS, zeta-potential, 19F-NMR, FTIR, TEM and UV-VIS measurements. As shown in Figure 1, the two coating strategies produced different hybrid nanostructures. Indeed, in one case we obtained NPs formed by a single Au core coated with a layer of polymer, while in the other the NPs were composed of several Au clusters covered by a coating film. Stability studies in biological fluids such as serum and human plasma were also performed. Overall, these systems can function simultaneously as 19F-MRI contrast agents and as drug delivery systems, resulting in promising theranostic agents for biomedical applications.
1. Doane, T.L. and C. Burda, Chemical Society Reviews, 2012. 41(7): p. 2885-2911.
2. Motamedi, S., et al., Biomedical optics express, 2011. 2(5): p. 1194.
3. Tirotta, I., et al., Journal of American Chemical Society, 2014, submitted.
claudia.pigliacelli@polimi.it