Aggregation rates in a shear flow were analyzed on the basis of trajectory analysis with non-linear Poisson Boltzmann (PB) solution used for the calculation of double layer force. The PB solution enables us to analyze the experimental data of orthokinetic aggregation of highly charged particles1,2 where linearized PB solution is not valid. Fig.1 shows the capture efficiency, which is defined as the ratio of actual aggregation rate to Smoluchowski’s one in shear flow, as a function of KCl concentration for different shear rate, G. Symbols are experimental values for sulfate latex particles with a diameter of 1.96 μm and a surface charge density of -60 mC/m2 taken from Sato et al.1, and lines are the theoretical values calculated with a Hamaker constant of 2.0×10-21 J. Fig.1 demonstrates that theoretical calculation qualitatively describes experimental data. However, theoretical values of CCC and capture efficiencies in fast coagulation regime are not quantitatively consistent with experimental ones. These discrepancies might be caused by the additional non-DLVO forces and charge heterogeneity which are not included in the present calculation.
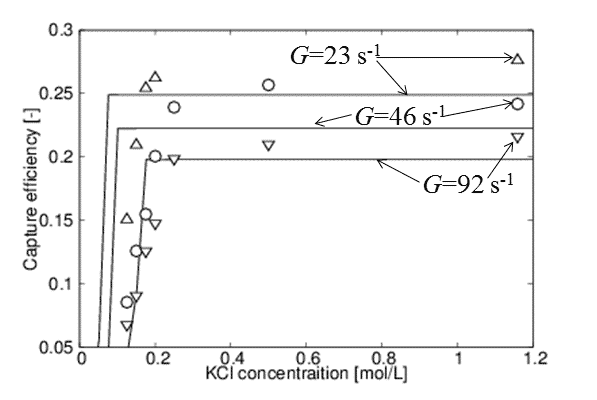
Fig.1 Capture efficiency vs. KCl concentration for sulfate latex with a diameter of 1.96 μm: Symbols and solid lines are experimental values taken from Sato et al. (2005) and theoretical values calculated by trajectory analysis with exact PB solution, respectively.
[1] D. Sato et al., Colloids Surf. A 266 (2005) 150-154.
[2] T. Sugimoto et al., Colloids Surf. A 443 (2014) 418-424.
s1321138@u.tsukuba.ac.jp