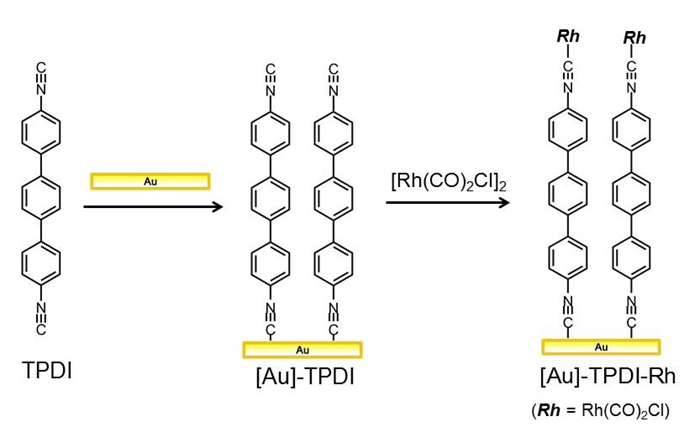
Self-assembling of organic molecules on surface automatically forms ordered densely packed molecular monolayer. This spontaneous phenomenon can be used as one of the promising low-cost methods to prepare functional materials. The most commonly used system is self-assembled monolayer of alkane thiolate on gold surface, whose application has been expanded to a wide range of functional devices including catalyst. We envisioned utilization of much less studied monolayers, monolayers of isocyanide, for catalyst preparation. We report herein the modification of gold surface with 4,4'-terphenylenediisocyanide (TPDI) as platforms for high turnover and selective Rh-catalyst in 1,4-hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
A gold surface evaporated on glass plate was immersed in a CHCl2 solution of TPDI to obtain the monolayer of TPDI on Au surface. The successive immersion in a benzene solution of [Rh(CO)2Cl]2 gave Rh-immobilized monolayers, [Au]-TPDI-Rh. Characterization of thus obtained surfaces was conducted by XPS, IR-RAS and ICP-MS.
The test reactions with 2-cyclohexene-1-one showed that [Au]-TPDI-Rh exhibits high selectivity to cyclohexanone over further reduced product, cyclohexanol. The selective 1,4-hydrogenation with Au-TPDI-Rh could be applied to a wide variety of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Typical catalyst turnover numbers are as high as in a rage of 50,000 to 150,000 per Rh atom grafted on the monolayer. The catalyst can be used repeatedly at least five times without obvious deactivation. The monolayer of diisocynide molecule on gold surface was thus confirmed as a useful platform for selective Rh-catalyzed hydrogenation reaction of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
hara@cat.hokudai.ac.jp