Cellulose solutions and hydrogels serve as a starting material for the preparation of cellulose beads - spherical particles having a diameter ranging from hundreds of nanometers, up to the millimeter scale. These may be used in many advanced applications such as chromatography over solid supported synthesis, protein immobilization and controlled drug delivery. Hydrogel shaping into spherical particles is realized by different methods: solution dropping into a coagulant, jet cutting, spinning drop atomization, spraying, ultrasonic dispersion techniques, etc.
We investigated the preparation of cellulose hydrogel dispersions in water or water/ionic liquid mixtures, fabricated either from cellulose solutions in ionic liquid or from macro-scale pure cellulose hydrogels of different concentrations.
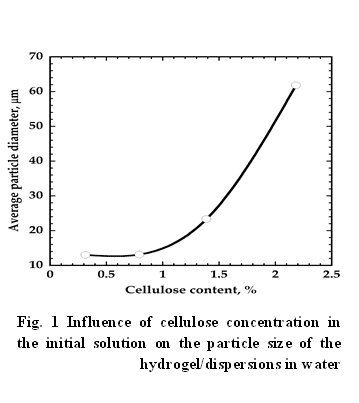
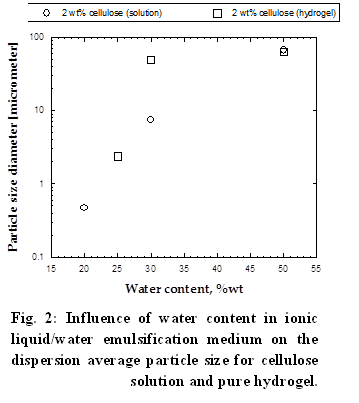
Based on our results, we can conclude that the most fine cellulose hydrogel dispersions can be obtained using a low concentration cellulose solutions (less than 2 wt. %) or hydrogels with a low cellulose content (less than 2 wt. %) in a dispersion medium consisting of an ionic liquid containing no more than 15 % of the water.