1. The problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interactions in hypersonic inlet
Three-dimensional shock wave interaction is a key problem for hypersonic three-dimensional inlet. Due to the complexity of shock configurations, there is not widely accepted analytical theory to such a problem. For example, in the corner flow of hypersonic three-dimensional compression inlet, the interaction of shock waves by two intersecting wedges may results in a regular shock reflection, or a complex Mach reflection with a bridge shock plane. The flow patterns induced by three-dimensional shock wave interactions are various according to different free-stream and shock conditions, which causes the difficulty to solve them analytically. Numerical simulation has been used to study the mechanisms of three-dimensional shock waves and their effects on the performance of hypersonic three-dimensional inlet. But, the analytical solution to the above problem is important and necessary to understand the fundamental mechanisms, and to design hypersonic inlet with better performance.
In this paper, the analytical approach to the problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interactions is concerned.
2. Analytical approach to the problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interactions
With a serial of sectional planes in the characteristic direction, three-dimensional steady shock wave interactions show spatial similarity, which implies that one of its spatial dimension can be transformed to a temporal dimension and the problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interaction may be transformed to that of two-dimensional moving shock wave interaction.
We will give the theoretic validation in this paper that the problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interaction can be indeed transformed to the problem of two-dimensional moving shock wave interaction. The characteristic planes is just perpendicular to the intersecting line of the two steady shock planes. As we have known, the problems of two-dimensional moving shock wave interaction have been thoroughly studied by Prof. Gabi Ben-Dor et al. in the last several decades. According to the theoretical analysis, various shock wave interactions phenomena exist in the problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interactions, which have their corresponding shock wave interaction configurations in that of two-dimensional shock wave moving shock wave interactions, such as regular reflection, Mach reflection and weak shock reflection, which have been summarized in the book of “Shock Wave Reflection Phenomena” by Prof. Gabi Ben-Dor.
The method of Shock-polar is very useful to analyze the shock interaction configurations in the two-dimensional moving shock wave interactions. These shock interaction configuractions have their corresponding shock configuration in the problem of three-dimensional steady shock wave interactions. Aslo, some shock interaction configurations do not observed in the two-dimensional steady shock wave interaction may exist in the three-dimensional steady shock wave interaction, such as Inverse-Mach reflection.
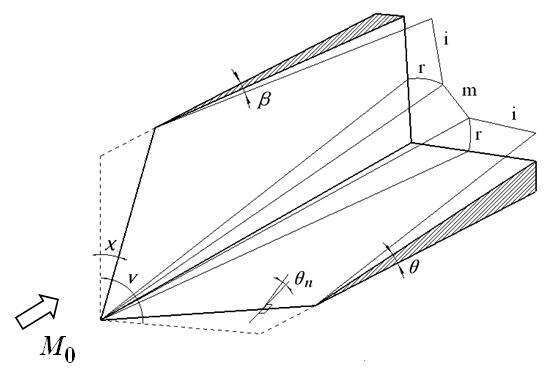
(a) Interaction of three-dimensional steady shock waves
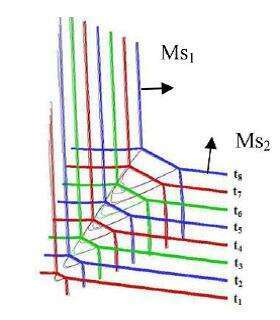
(b) Interaction of two-dimensional moving shock waves
Fig.1 The moving shock analytical approach to the interaction of three-dimensional shock waves
3. The role of shock dynamics
Shock dynamics is a powerful analytic tool to analyze the problem of two-dimensional moving shock wave interaction. Also, shock dynamics give a simplified analytical approach to the bridge shock plane induced by three-dimensional steady shock wave interaction by introducing the "virtual wall" concept.
References
[1] Yang Yang. Investigations on the complex flows induced by three-dimensional shock interactions, Ph.D. Thesis of Institute of Mechanics, CAS.
[2] G. Ben-Dor. Shock Wave Reflection Phenomena. 2nd ed. Springer Berlin Heideberg, New York, 2007.
[3] Chun Wang, Yang Yang , Gaoxiang Xiang and Zonglin Jiang, The Progress in Shock Dynamics, The Seventh Across-Strait Workshop on Shock/Vortex Interaction, Tamshui, 2014.

