The production technique of mechanoactivated energetic composition (MAEC) based on ammonium perchlorate (AP) and aluminum has been developed. For preparation of the mixtures, regular powders of AP (20-100 microns), and Al powders - pyrotechnic powder PP-2 (flake particles 50 - 200 microns by thickness 2-5 microns) and Al(8) (average size of particles ~ 280 nm) were used. The components were mixed and activated an Activator-2SL planetary ball mill (JSC "Activator", Novosibirsk) with steel balls and drums and with water cooling. The optimum conditions of mechanical activation were found so that the maximum homogenization of the mixture was provided in the absence of the reaction between reagents. The structure of MAEC was studied by X-ray diffraction analysis and scanning electron microscopy. The results of research of explosive properties (deflagration to detonation transition DDT in Al/AP loose-packed charges, dependence of detonation velocity (DV) on density for the pressed charges and mechanical sensitivity) have been received.
Mechanical sensitivity was investigated by the method of the collapsing shell. The value of critical pressure Pcr corresponding to the transition from mechanical destruction of charges in the shell of PMMA without an explosion to destruction with explosion was measured. For activated Al/AP (20/80) Pcr = 0.61 GPa and occupies an intermediate position between such sensitive explosives as bis(trinitroethyl)nitramine and lead azide.
The study of DDT was carried out in steel and duralumin tubes with a diameter of 10 mm at a porosity of samples about 80%. Measurements of DV for Al/AP were carried out at a distance of 80 mm from the point of ignition. With increasing activation time Tact from 2 to 10 min the process speed increases sharply from 100 to 2700 m/s and with a further Tact increasing DV gradually decreases to 2300 m/s. D(Tact) for MAEC Al/AP (20/80) is shown in Fig. 1.
The results of measurements of speed of a detonation depending on density of the pressed charges of MAEC Al/AP 20/80 are shown on Fig. 2. The DV maximum has been received for MAEC with a ratio of components Al/AP 20/80. In comparison with data for usual mixtures Al/AP [1] mechanoactivated composites show essentially higher DV that can be connected with increase in reactionary ability of the activated mixes in the course of a detonation.
References
- Donna Price, A.R. Clairmont, J.O. Erkman. Explosive Behavior of Aluminized Ammonium Perchlorate. Naval Ordnance Laboratory Report NOLTR 72-15, White Oak, MD, USA, 1972.

Fig. 1: Dependence of detonation velocity of loose-packed charges Al/AP (20/80) on the activation time.
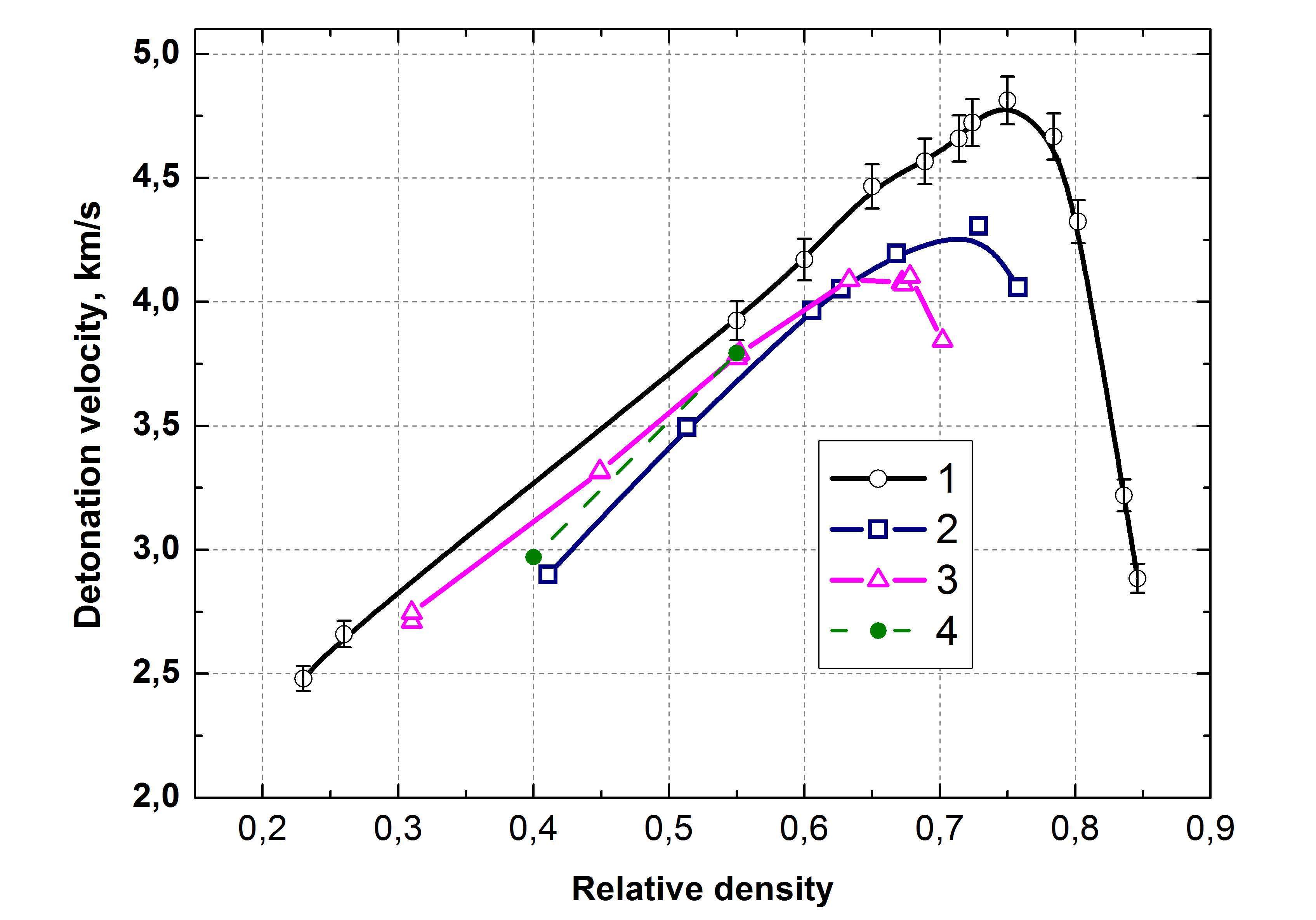
Fig. 2: Dependence of detonation velocity of on the relative density. 1 - MAEC Al/AP 20/80, Donna Price data [1] - 2 - AP, 3 - Al/AP 10/90, 4 - Al/AP 20/80

