
A Parameter Study of Shock Focusing Phenomenon for Shock-Elliptic Bubble Interaction
|
 |
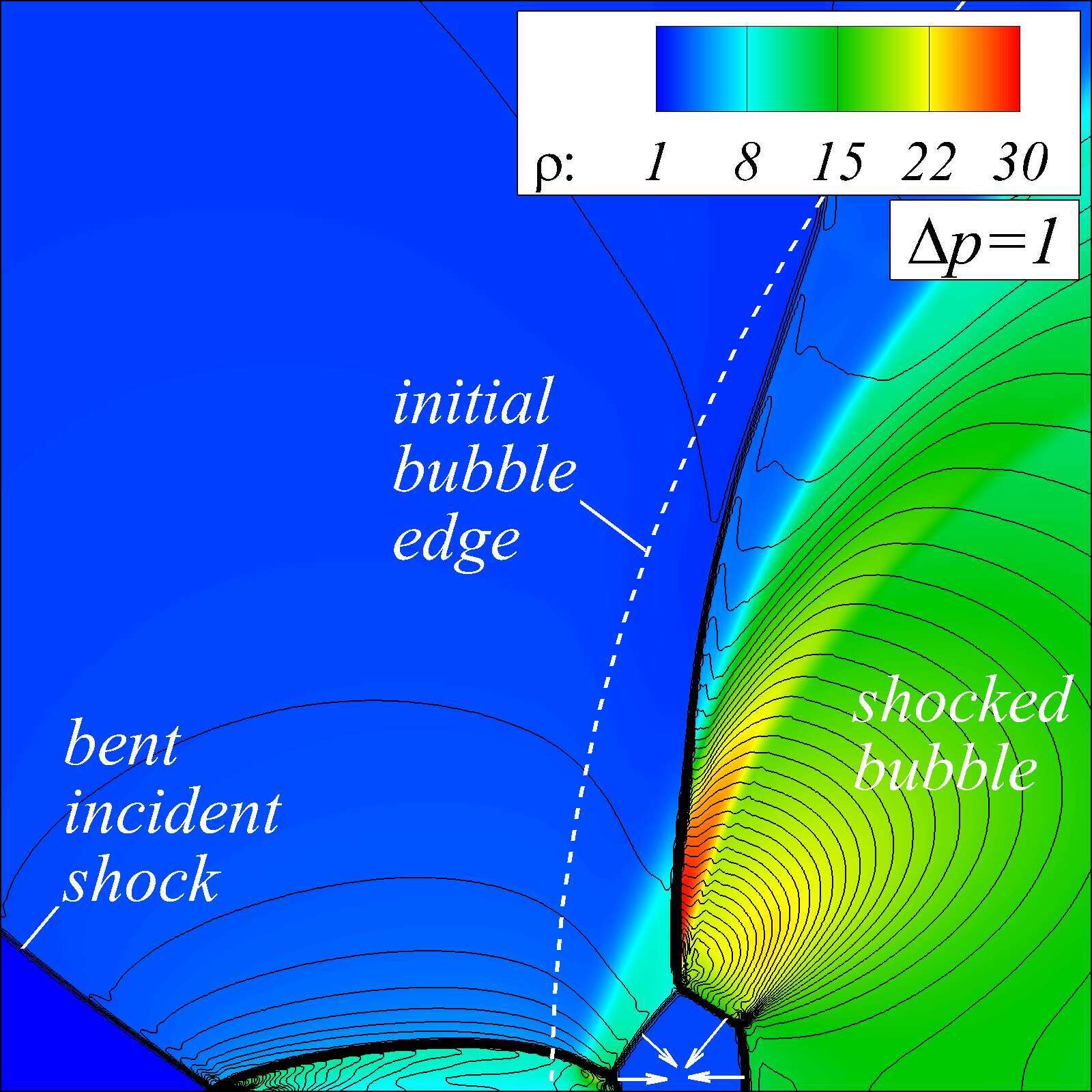 |
Fig. 1 An internal SFP pattern for converging shock refraction case (M=2, A=0.5, e=1.4): early stage (left) and shortly before the cumulation (right). Bottom edge is the axis of symmetry; white arrows indicate local shock propagation directions.
The present study continues and expands the investigation [1] of interaction of a shock with elliptical bubbles using Euler’s equations. A parameter study is performed for Mach number, Atwood number and bubble shape. A qualitative dependence of SFP pattern type and intensity is determined (see Fig. 2 for an example for A=0.5). Three-dimensional simulations are performed in order to determine non-axisymmetrical features of SBI-induced shock focusing process.
This study is supported by Russian Scientific Fond (project №14-11-00773).
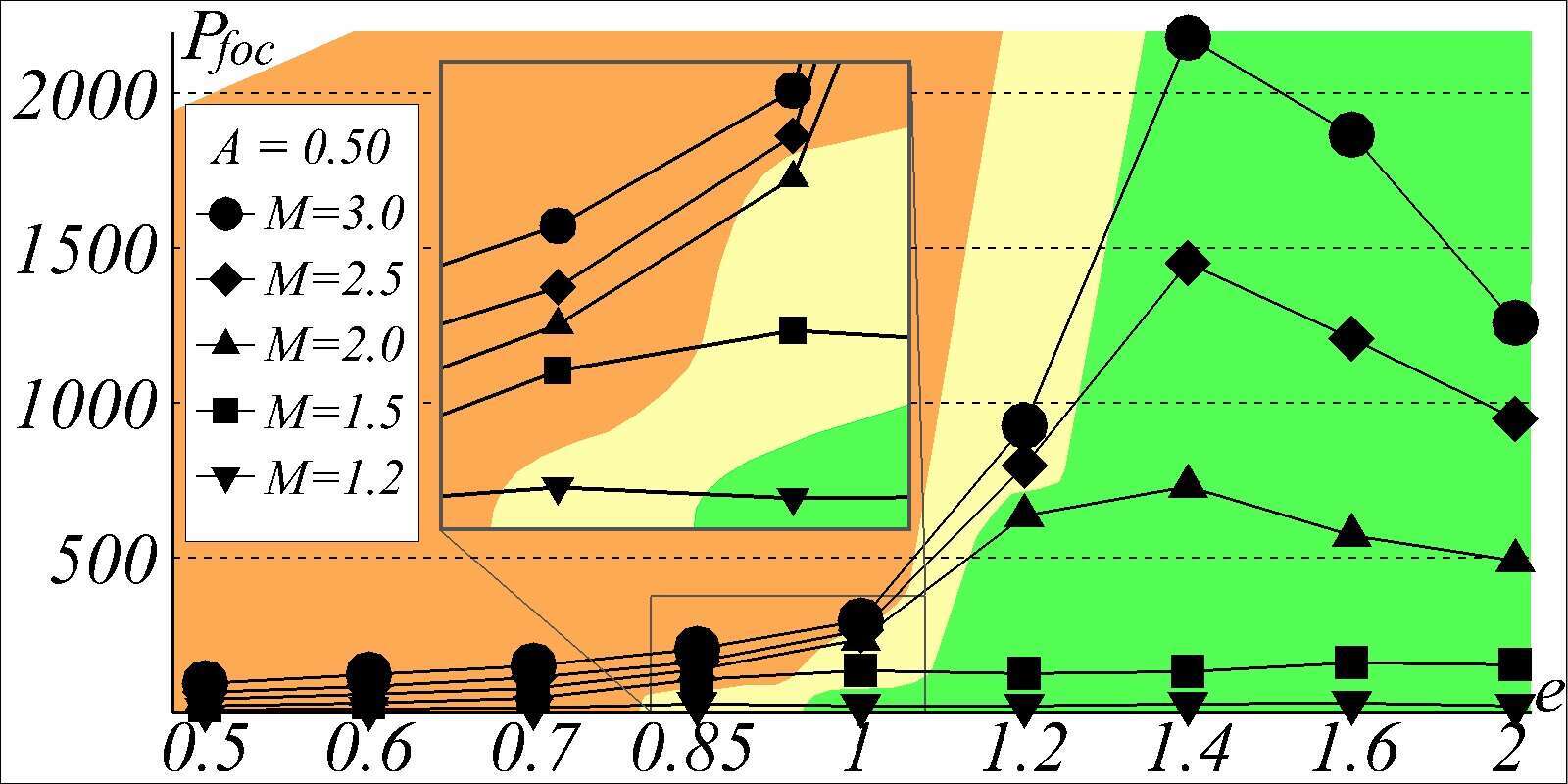
Fig. 2 A qualitative dependence of SFP pattern and peak pressure on Mach number M and bubble elongation e for A=0.5. Patterns are coded by color: orange is external, yellow is transitional and green is internal cumulation type.
1. Georgievskii P.Yu., Levin V.A., Sutyrin O.G. Cumulation Effect upon the Interaction between a Shock and a Local Gas Region with Elevated or Lowered Density // Fluid Dynamics. 2011. V. 46. No. 6 P. 967–974. DOI: 10.1134/S0015462811060147
Powered by Eventact EMS