Background: Dyslipidemia is an independent major risk factor for the development of coronary artery disease(CAD). Statins are the cornerstone for primary and secondary prevention of CAD.
Aim: To describe trends in statin use and lipid profile between the years 2002-2013 in a large cohort of patients admitted with an acute coronary syndrome(ACS).
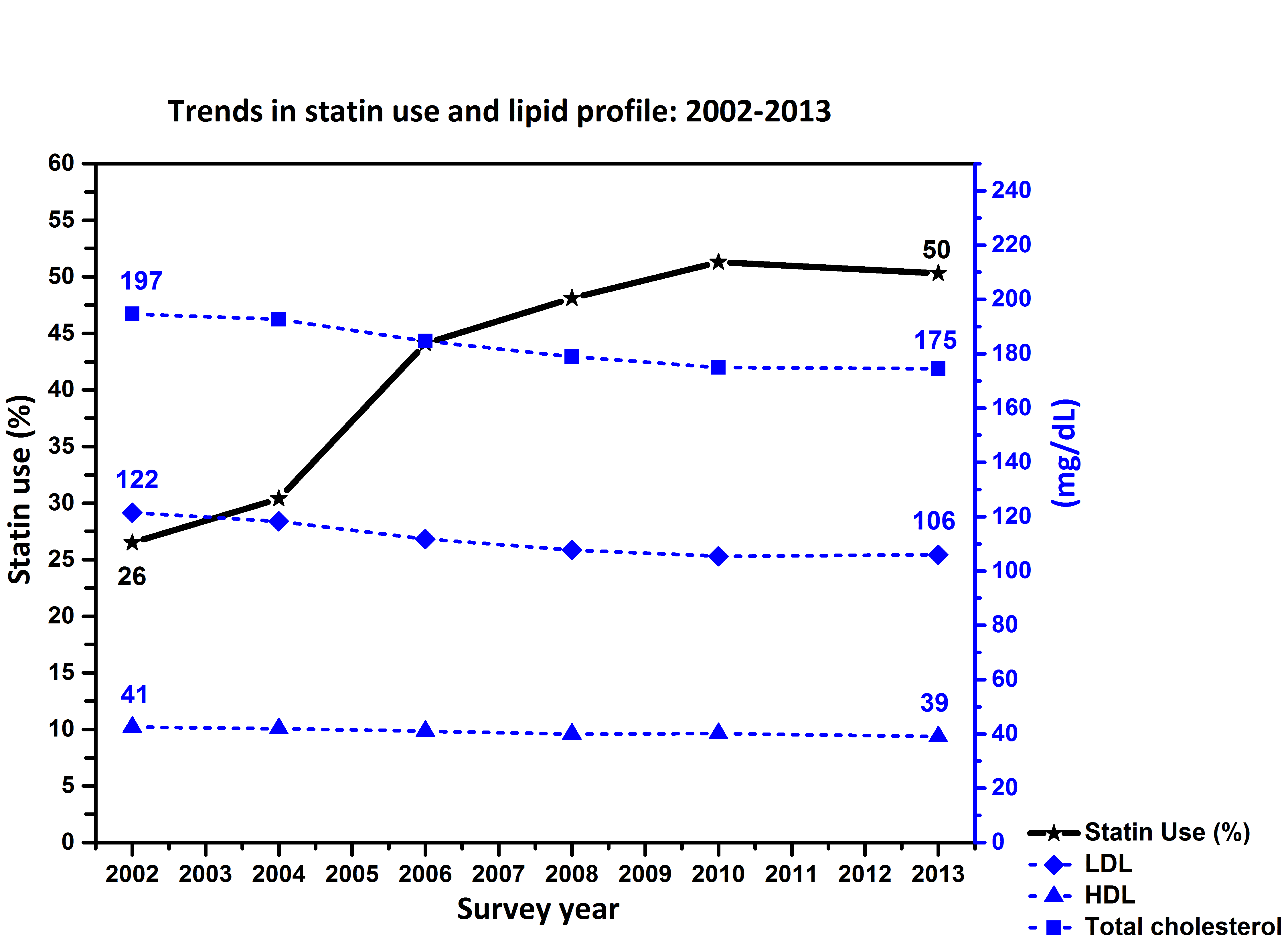
Methods: Data was drawn from 6 consecutive ACS Israeli surveys(ACSIS), performed between the years 2002-2013 in Israel. Lipid profile on admission(total cholesterol [TC], LDL-C and HDL-C) and the use of statins prior to the index hospitalization were determined for the total cohort and for subgroups with or without prior CAD.
Results: From 2002 to 2013, use of statins prior to the index ACS event steadily increased and was paralleled by a decline in TC, LDL-C and HDL-C (Figure, p for trend<0.0001). Among patients with CAD, TC declined from 192mg/dl in 2002 to 160 mg/dl in 2013, and LDL-C declined from 116mg/dl to 93 mg/dl, respectively (p for trend<0.0001). Among patients without CAD,TC declined from 199.9 mg/dl in 2002 to 183mg/dl in 2013, and LDL-C declined from 125 mg/dl to 114 mg/dl, respectively (p for trend <0.0001).
Conclusions: Among patients admitted with an ACS during the last decade, better adherence to guidelines with increasing use of statins prior to the index ACS event was noted, that was paralleled by an improvement in lipid profile. These findings have relevance for primary and secondary prevention.

