
Collective Light Scattering on Gold Nano-Spheres in Micro-Droplets of Suspension
We study scattering of light on evaporating single microdroplet of suspension of gold inclusions (125nm radius) in glycol (DEG). The optical diagnostics of a single droplet levitating in the electrodynamic trap was based on the analysis of the spatial interference pattern and temporal distributions of the scattered light intensity
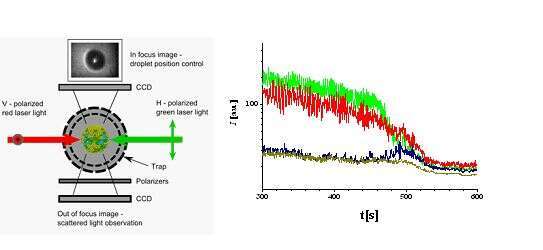
Fig.1 Outline of experimental set-up (let) and (right)the evolution of intensities IVV (red), IHH (green), IVH (blue) and IHV (dark yellow). Cross polarized intensities IVH, and IHV are small but substantial. Fast oscillations of intensities IVV and IHH are due to the droplet WGM, magnified in the inset.
The intensity of scattered depolarized light was used to determine effective index of refrac-ion of the medium surrounding inclusions. The resonant increase of scattered light intensity was observed in the region of overlap inclusions mean distance and light wavelength (on Fig 1 near t=500s). Observed resonances were interpreted as collective scattering (CS) of plasmons induced in different inclusions showing importance of influence of nonlocal fields on local field scattered by given inclusion. More than double increase of scattered light intensity was observed for “high” preliminary density of inclusions (ca.1500 inclusions) at resonance. The oscillatory shape of CS resonances showed constructive (in phase) and partly destructive interference of plasmons in separate inclusions on collective oscillations . Observed CS resonances were modulated by whispering gallery modes (cavity modes of droplet acting as a spherical resonator[1]) showing ultra narrow structure of CS resonance connected with droplet cavity modes (WGM). The property of very narrow and relatively strong resonances giving possibility to tune scattering in very precise manner seems to be extremely interesting feature for future studies and possible applications.
[1] Kolwas, M.; Jakubczyk, D.; Derkachov, G. and Kolwas, K. J.Q.S.R.T. 2013, 131(0), 138 – 145
kolwas@ifpan.edu.pl
Powered by Eventact EMS