
Lasing Characteristics of Two Dimensional DFB Surface Plasmon Lasers
We experimentally study surface plasmon (SP) lasing at telecom wavelength (λ ∼ 1.5 μm) in a series of metal hole arrays on a gold-semiconductor interface. This system is operating in an extreme regime, with both very high loss and gain, much higher than in most semiconductor lasers.
The optically pumped semiconductor serves as in-plane SP source and delivers enough gain to compensate the losses of the SP and even facilitates laser operation [1]. The sub-wavelength holes are arranged in a square lattice and deliver the distributed feedback (DFB) required for laser action. These systems resembles 2D photonic crystals, in which SP-to-SP scattering [2] on the holes couples traveling SP waves into plasmonic bands. We experimentally determined the gain and loss of these plasmonic bands [3].
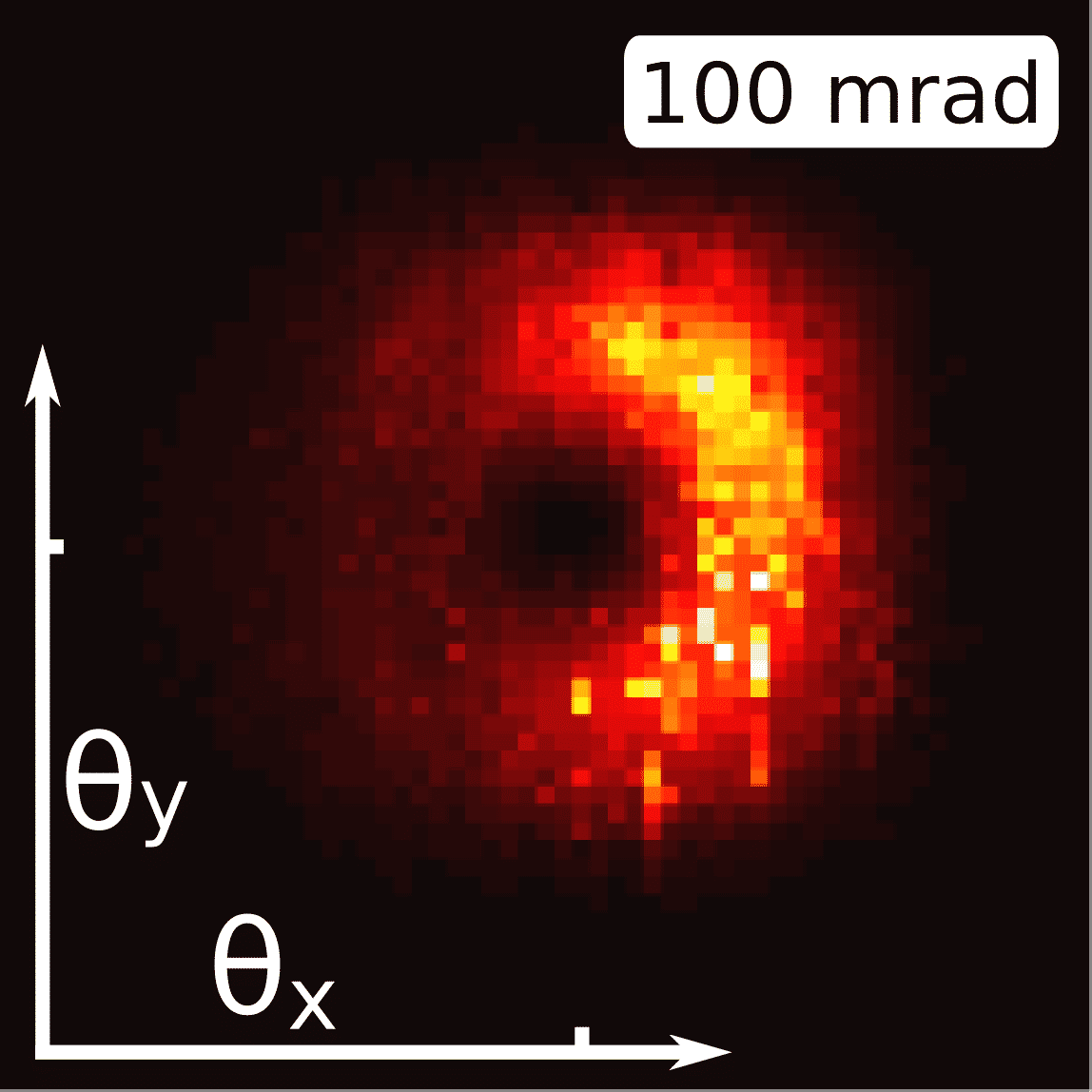
Here we study in-plane SP lasing in the “dark” plasmonic bands, which results in far field emission that resembles a radially-polarized vector-vortex-beam, as shown in Figure 1. We present a study on the spatial coherence of the emission and laser characteristics of these 2D DFB SP lasers, such as multi-mode behavior and spectral narrowing.
[1] F. van Beijnum, P. J. van Veldhoven, E. J. Geluk, M. J. A. de Dood, G. W. ’t Hooft, and M. P. van Exter, “Surface Plasmon Lasing Observed in Metal Hole Arrays”, Physical Review Letters, vol. 110, no. 20, May 2013.
[2] M. P. van Exter, V. T. Tenner, F. van Beijnum, M. J. A. de Dood, P. J. van Veldhoven, E. J. Geluk, and G. W. ’t Hooft, “Surface plasmon dispersion in metal hole array lasers”, Optics Express, vol. 21, no. 22, p. 27422, Nov. 2013.
[3] V. T. Tenner, A. N. van Delft, M. J. A. de Dood, and M. P. van Exter, “Loss and scattering of surface plasmon polaritons on optically-pumped hole arrays”, Journal of Optics, vol. 16, no. 11, p. 114019, Nov. 2014.
Powered by Eventact EMS