Introduction
Loop diuretics are considered as first line therapy in the relief of volume overload in both systolic and diastolic heart failure. However, in some patients unresponsive to loop diuretics, combination therapy with oral thiazide diuretics is helpful due to the additional distal tubule blockade. In 2013, the import of metolazone to Israel was officially discontinued and it is currently unavailable in most pharmacies. We hypothesized that hydrochlorothiazide (50mg) may be safe and effective as metolazone (5mg) in patients hospitalized with heart failure.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated patients who were hospitalized in Carmel medical center, Haifa, Israel during 1.1. 2014- 12.2014 and received either metolazone 5mg or hydrochlorothiazide 50mg according to pharmacy records. Only patients with heart failure and concomitant loop diuretic therapy (furosemide) were included. We then compared between the 2 groups in terms of weight loss, urine output, potassium depletion and worsening renal failure.
Results
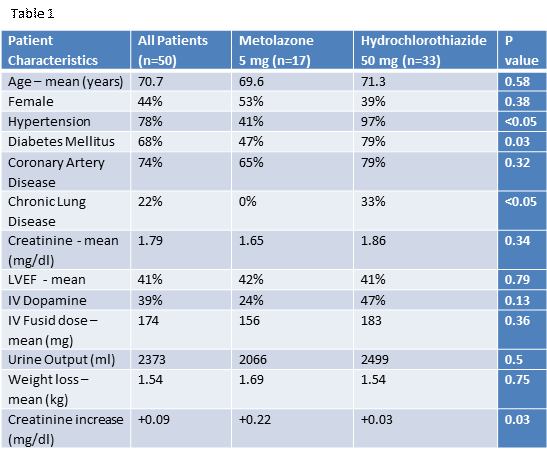
A total of 50 patients with a diagnosis of heart failure received either 5mg metolazone or 50mg hydrochlorothiazide in addition to furosemide during the study period (after excluding patients without follow up of weight, electrolytes or urine output). Baseline characteristics of both groups are shown in table 1. The hydrochlorothiazide group had a higher incidence of hypertension, diabetes and COPD. There were no other significant baseline differences between the 2 groups, including LV ejection fraction, dopamine use or renal failure. The differences in urine output (2066 ml versus 2499 ml P=0.5) and weight loss (1.69 Kg versus 1.54 Kg P=0.75) between the metolazone and hydrochlorothiazide groups respectively, were non-significant. Severe hypokalemia was observed only in 2 patients – one in each group.
Conclusions
Hydrochlorothiazide 50mg in addition to furosemide is as safe and effective as metolazone 5mg. This is a suitable alternative and provides a reasonable solution to the metolazone shortage in Israel.