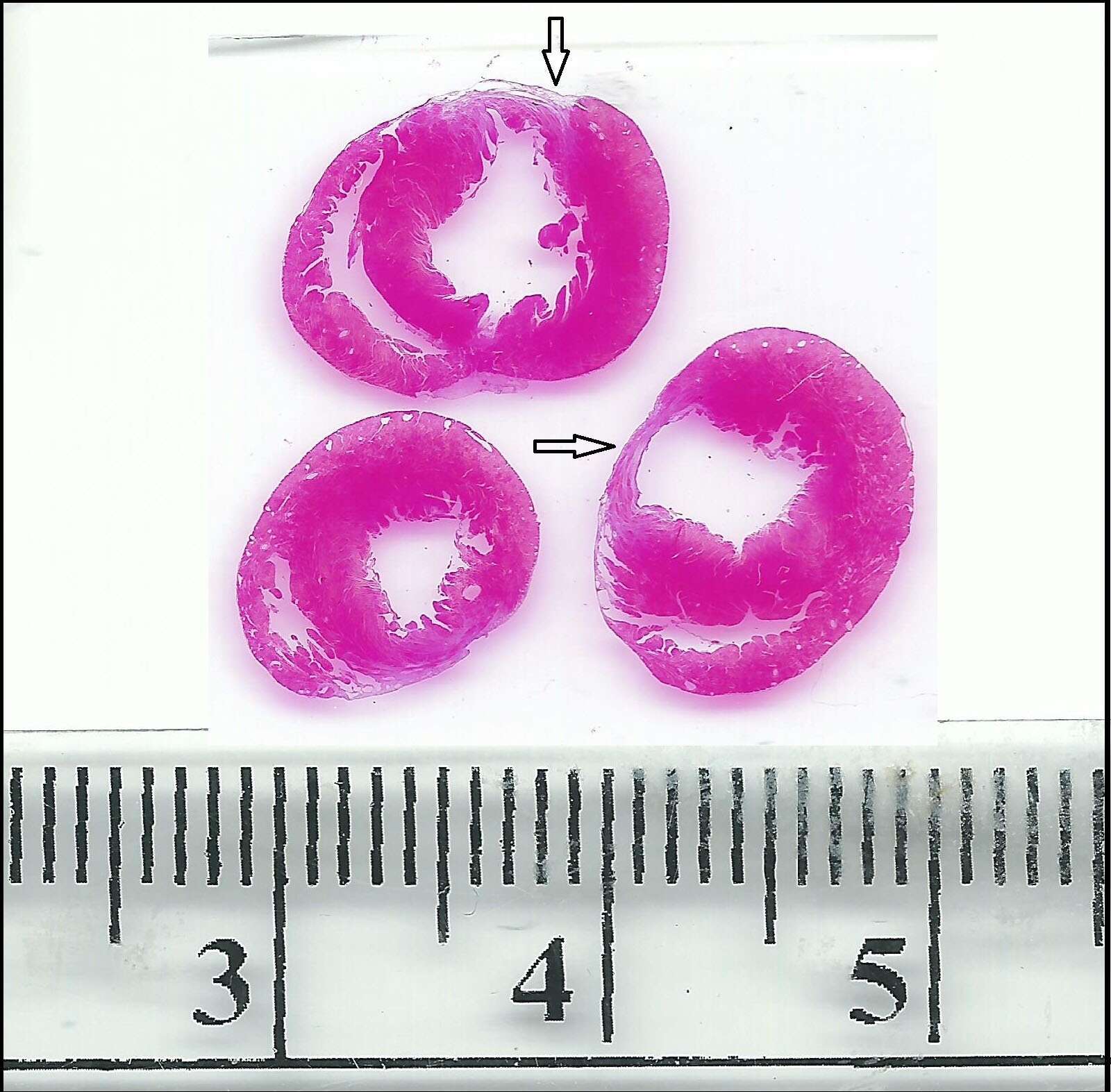
Background: Irreversible electroporation (IRE) is an emerging cell ablation modality based on the biophysical phenomenon of electroporation. The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the in vivo safety and efficiency of several different IRE protocols. Methods: In-vivo IRE was applied using two needle electrodes in an open thoracotomy rodent model. An in vivo experiment (N=43) compared the extent of myocardial damage of seven different IRE protocols with a rodent model of anterior myocardial infarction (MI). Animals were divided to four groups: low potency (N=17), high potency (N=14), MI (N=7) and control (N=5). All animals underwent baseline echocardiographic evaluation . Degree of myocardial ablation was determined using repeated echocardiography measurements in day 7 and day 28 as well as histologic analysis at day 28. ANOVA statistical method was used to compare echocardiographic and morphometric results. Results: Animal survival was 100%, during 28 days of follow up. Compared with baseline echocardiography, both low and high potency IRE protocols demonstrated significant change in LV echocardiographic parameters at 7 and 28 days. On day 7 ejection fraction was: 65%±5%, 48%±9%, 42%±17%, 52%±16 in the control, low potency, high potency, and MI group, respectively (p = 0.014). Similarly, fractional shortening was 37%±4%, 25%±6%,22%±10%,28%±10% in the groups above respectively (p = 0.11). Histologic analysis at 28 days demonstrated that the percentage of scarred myocardium area was 2%±3%, 9%±5%, 10%±9% and 32%±19% in the groups above respectively (p<0.001). Compared with normal myocardium, thickness of damaged myocardium was reduced by 3%±4% , 8%±6%,14%±10%,32%±20% in the groups above respectively (p<0.001). Conclusions: IRE is an efficient modality for in vivo myocardial ablation. Changes in IRE protocols can be used to limit or extend that volume of myocardial ablation. IRE might be used in a transcatheter approach for myocardial volume reduction in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy