
Beyond Planar Plasmonics: Skew 3D Nanoantenna Arrays
Metallic nanoantennas have received a wide interest in the plasmonic community in the past two decades since it was realized that they produce a number of very useful and tailorable optical phenomena [1]. While most of the literature focused on planar antenna geometries, in this work we consider a new 3D spatial arrangement of silver antenna dimers lying on a silver baseplate.
A scheme of the antenna layout is reported in Fig. 1a, along with the geometrical parameters considered. These and various other 3D architectures can be easily realized by means of a recently presented fabrication technique based on focused ion beam milling [2]. The technique relies on the high energy secondary electrons produced during the process of focused beam milling, we refer to [2] for further details. A scanning electron microscope image of the fabricated structures is reported in Fig. 1b. These antennas are characterized by a non zero tilt angle (α) with respect to the normal and possibly by non-zero angle between the antenna planes, β (see Fig. 1a).
Finite elements electromagnetic simulations will be presented describing the near and far field properties of this dimer antenna configuration, showing that interesting field enhancement and diffractive coupling effects can be obtained, owing to the two independent resonant eigenmodes of this structure. Experimental far field characterizations of the structure will be also presented, in excellent agreement with simulations.
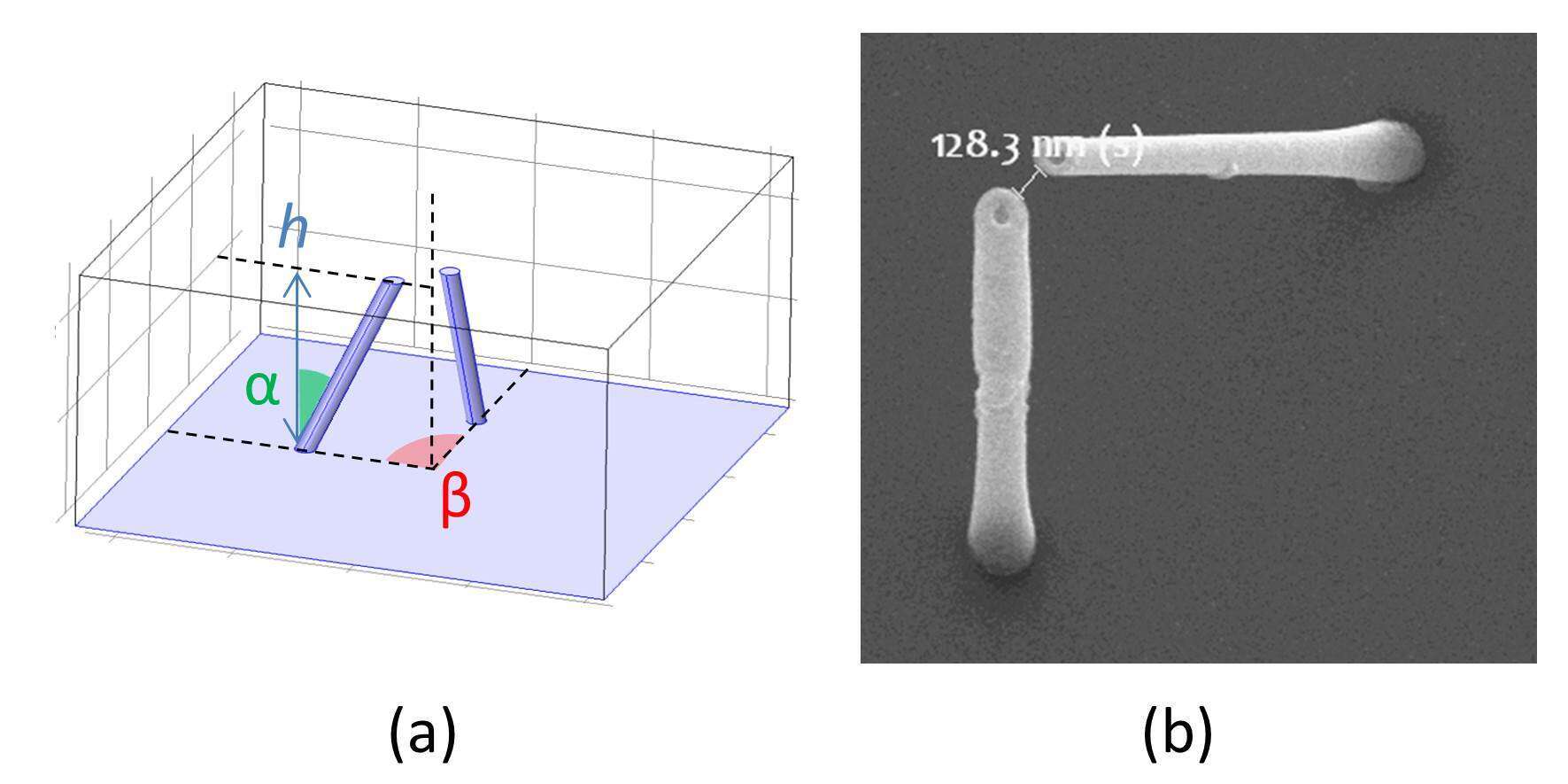
Fig. 1. (a) 3D scheme of the considered antenna dimers. Geometrical parameters are h=1.8μm, α=32°, β=90°, pitch = 4.5μm, g=130nm; (b) SEM micrograph of a fabricated dimer.
[1] S. Panaro, et al. ACS Photonics, 1, 310-314 (2014).
[2] F. De Angelis, et al. Nano Lett. 13 (8), 3553-3558 (2013).
francesco.deangelis@iit.it
Powered by Eventact EMS